River System of India – Ganga River System
| Prime Watershed of River Origin in India |
|
| River categories on the basis of their origin |
|
| Top 5 largest rivers of India | Ganga > Godavari > Krishna > Yamuna > Brahmaputra |
Ganga River System
| Ganga Tributaries | Yamuna, Gomti, Ghaghara, Gandak, Kosi, Son, Tons & Punpun |
| Ghaghara Tributaries | Sarda & Rakti |
| Kosi Tributaries | Arun, Tamur & Sun Koshi |
| Yamuna Tributaries | Chambal, Sind, Betwa & Ken |
| Chambal Tributaries | Kali Sindh, Parvati & Banas |
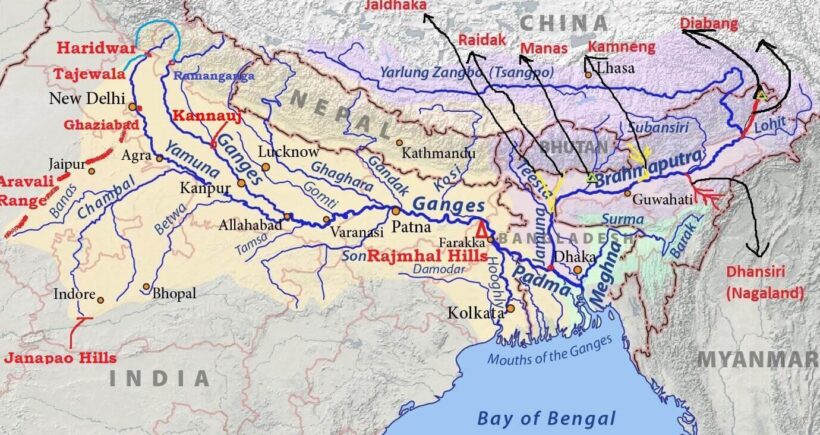
River Ganga
- Origin > As Bhagirathi from Gangotri Glacier (Uttarkashi – Uttarakhand)
- Alakananda unites with Bhagirathi at Devprayag, Uttarakhand > Henceforth known as Ganga
- Passing through Rishikesh, it debounches in plains of Haridwar
- From Haridwar, it flows Southward to reach Allahabad where it joins Yamuna
- Near Rajmahal Hills, it turns southeast & bifurcate at Farraka into Hoogly (Kolkata) & Padma (BD)
- At Bangladesh, Ganga merges with Brahmaputra (Known as Jamuna in Bangladesh) at Goalundo Ghats
- Mixture is known as Padma River
- Then it merges with Meghna & finally falls in Bay of Bengal
- Meghna > Known as Barack river in India
- Major tributaries > Yamuna, Gomti, Ghaghara, Gandak, Kosi, Son, Tons & Punpun
Major Tributaries of Ganga River System
| Ghaghara |
|
| Gandak |
|
| Kosi |
|
| Son |
|
| Gomti |
|
| Yamuna |
|
| Betwa |
|
| Ken |
|
| Chambal |
|
| Banas |
|
| Damodar |
|
For more updates, explore the Geography . Feel free to share your thoughts and comments.
If you’re passionate about building a successful blogging website, check out this helpful guide at Coding Tag – How to Start a Successful Blog. It offers practical steps and expert tips to kickstart your blogging journey!










4 comments
thankyou very much to share the knowledge.
The largest river in India is Indus river not Ganga.
INDUS RIVER FLOWS ABOUT 709 KM / 2882KM SO LARGEST RIVER IS GANGA
Tons is tributary(largest) of Yamuna not Ganga as mentioned.
Thank you.