TMT, SMAP, GOCE, MAST
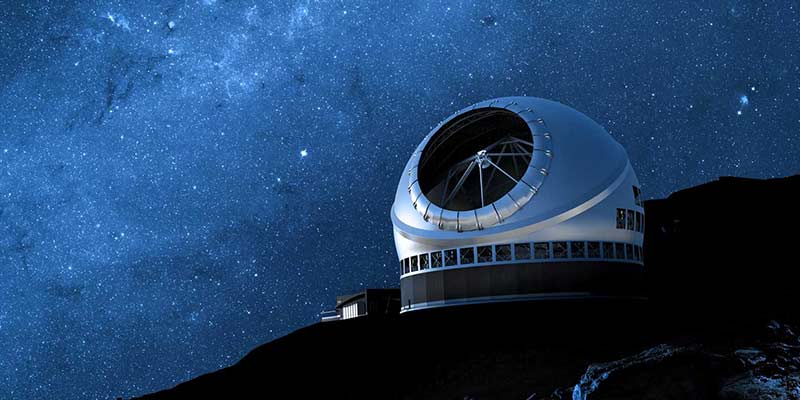
Thirty Meter Telescope (TMT)
- Mauna Kea volcano summit, in Hawaii; will be finished by 2020
- Partner countries – India, US, Canada, Japan, China
- Cost of the Project – $ 1.5 billion
Key Features of TMT
- World’s largest infrared + optical telescope – because its primary mirror is 30 m wide.
- Will help finding most distant and oldest stars that were born after Big Bang, Thus we can learn more about the origin of the universe.
India’s contribution to TMT project
- 10% finance (1300 crore)
- Mirror-coating & polishing of this telescope
- Will develop the control system, sensors, fabrication, actuator systems
- 100 / 492 smaller, hexagonal mirrors, needed to build the 30m diameter primary mirror of the telescope
Indian astronomers will be allowed to use this telescope for the time proportional to India’s contribution (10%). Japanese will get to use it for 25% and so on.
Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) : NASA’s first satellite to collect global soil moisture
- Designed to measure the moisture of Earth’s dirt accurately + a global map of the planet’s soil moisture levels every three days
- Built to measure moisture in the top 2 inches of soil
Benefits of SMAP
- To better forecast crop yields and assist in global famine early-warning systems
- create more accurate weather models
- learn more about drought conditions & even predict floods
Goce gravity boost to geothermal hunt
- GOCE was the 1st of European satellites intended to map unprecedented detail the Earth’s gravity field.
- It mapped Earth’s gravity field from 2009 to 2013 at high resolution.
- Information about variations in gravity across the planet could help prospectors find promising locations where sub-surface heat can be exploited to generate electricity.
- Goce’s maps are expected to shortcut some of the effort by pinpointing regions of the world with the best characteristics, such as where the continental crust is at its thinnest.
Geothermal energy is clean and sustainable heat from the Earth. This keen sensing is expected to narrow the search for prime spots to put future power stations.
Multi Application Solar Telescope (MAST)
- Aimed at detailed study of the Solar activity including its magnetic field.
- This study of solar activities would facilitate space weather predictions in the future.
- Capable of capturing three-dimensional aspects of the solar magnetic fields further enabling the scientists to get a better understanding of the solar flares and eruptions taking place in such twisted magnetic fields.
- USO is a part of Physical Research Laboratory (PRL), which is an autonomous unit of the Department of Space.
- The observatory is situated on an island in the middle of Fatehsagar lake at Udaipur
Why observatory is made in the middle of lake?
- Large water body surrounding the telescopes decreases the amount of heating of the surface layers.
- This decreases the turbulence in the air mass and thereby improves the image quality and seeing.
Features of MAST
- 50 cm aperture
- Off-axis Gregorian-Coude telescope
Other Telescopes in India
- National Large Solar Telescope – proposed @ Merak Village, Ladakh
- ARIES Observatory – Nainital
- Solar Tunnel Telescope, Kodaikanal Solar Observatory @ Kodaikanal
For more updates, explore the Sci Tech. Feel free to share your thoughts and comments.
If you’re passionate about building a successful blogging website, check out this helpful guide at Coding Tag – How to Start a Successful Blog. It offers practical steps and expert tips to kickstart your blogging journey!