Open Defecation India, Swachh Bharat Mission
Open Defecation Idea
India accounts for 59 % of total people in the world who practice open defecation, & 90 % of people in south Asia. Swachhta Status Report in 2015, more than half of the rural population still defecates in open.
Problems associated with open defecation
- Malnutrition, Diarrhoea and worm infection
- Open defecation puts at risk the dignity of women – Women feel constrained to relieve themselves only under the cover of dark – make them more prone to physical attacks
- Cripples national development – workers produce less, live shorter lives, save and invest less
Challenges faced
- Traditional practice – It is deeply ingrained in society
- Sanitation is not a socially acceptable topic, and hence, people do not discuss it
- Many of the poorest people do not prioritize toilets; many are living in rented homes without toilets
- Society does not view lack of a toilet as unacceptable. Building & owning a toilet is not perceived an aspiration
- Construction of toilets is still seen as the government’s responsibility
The challenge is to motivate people to see a toilet as fundamental to their social standing, status and well-being. The success of Swachh Bharat Mission is dependent upon behavioral changes and thus there is a need to engage with the community and facilitate the efforts by the people and involved organisations.
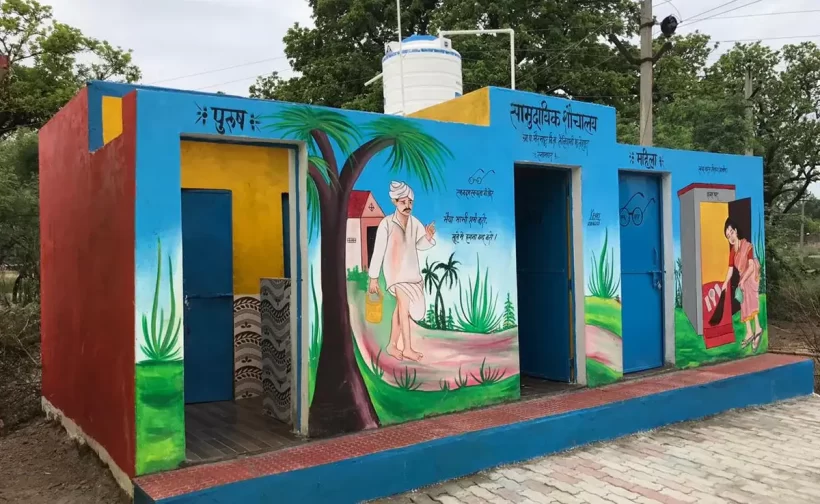
Swachh Bharat Mission
It was launched on 2 October 2014 to make India clean and open defecation free by 2019, Mahatma Gandhi’s 150th birth anniversary. It has slowly developed into a people’s movement with greater awareness and participation and increased interdepartmental coordination.
- Ministry for Drinking Water and Sanitation is looking at the rural part of the scheme
- Urban Development Ministry is implementing the programme in urban areas
Efforts by the government
- Cash incentive for building toilets are being provided by the government
- Creating solid waste management facilities
- Efforts and focus on bringing behavioral changes by –
- Roping in celebrities to promote
- City surveys to instill a sense of competition among cities – Swachh Survekshan
- Using technology like Hike Messenger Group which has local administrators from the respective states showcasing their achievements
- Creation of a portal by the ministry where all the information is available about the project
- Sanitation Messengers (Swachchata Doot)- village level motivators
✅ 10 Key Points on Open Defecation in India & Swachh Bharat Mission:
-
Open Defecation in India:
-
India accounted for the highest number of people practicing open defecation globally, especially in rural areas.
-
-
Consequences of Open Defecation:
-
Causes water contamination, spread of diseases like diarrhea, typhoid, cholera, stunting in children, and safety issues for women.
-
-
Launch of Swachh Bharat Mission (SBM):
-
Launched in 2014 to make India Open Defecation Free (ODF) by October 2, 2019, marking Gandhi’s 150th birth anniversary.
-
-
Objectives of SBM:
-
Construction of toilets, promoting hygiene, solid and liquid waste management, and behavior change.
-
-
Achievements of SBM:
-
Over 110 million toilets built; most villages, districts, and states declared ODF.
-
-
Behavior Change as Key Challenge:
-
Infrastructure creation alone was insufficient; efforts focused on community-led awareness and behavior transformation.
-
-
Swachh Bharat Mission Urban & Rural:
-
SBM-Gramin focused on rural areas.
-
SBM-Urban targeted urban cleanliness, waste management, and public sanitation.
-
-
SBM 2.0 (2021-2026):
-
Aims to sustain ODF status, improve solid and liquid waste management, and ensure sustainable sanitation systems.
-
-
Criticism & Gaps:
-
Reports of toilet non-usage, lack of water in toilets, and false ODF claims in some areas.
-
-
Way Forward:
-
Ensure sustainability of ODF status, robust monitoring, capacity building, and integrating sanitation with health, education, and water conservation programs.
-
For more updates, explore the Social Issues. Feel free to share your thoughts and comments.
If you’re passionate about building a successful blogging website, check out this helpful guide at Coding Tag – How to Start a Successful Blog. It offers practical steps and expert tips to kickstart your blogging journey!







1 comment
verf good effort