INO, PROVe, TOPs, NISAR
Polar Remotely Operated Vehicle (PROVe)
- India’s first Polar Remotely Operated Vehicle (PROVe) operationalized in North Antarctica
- Indigenously built by National Institute of Ocean Technology (NIOT) under Union Ministry of Earth Sciences
- Will measure parameters like ocean currents, temperature, dissolved oxygen and salinity in the Antarctic
- Monsoon prediction and reading of pattern will become easier
- Capable of probing the sea bed under normal temperature and exploring up to 200 meters in inhospitable and tough regions
- Successfully deployed in Priyadarshini Lake (Antarctica) by ESSO -NIOT
- ESSO-NIOT – An Indo-US initiative under the Monsoon Mission program of the Union Ministry of Earth Sciences
- Studying science behind the monsoonal events of Bay of Bengal using both Indian & US research ships
Significance of PROVe
- The results and outcomes will help researchers in understanding the biological activities taking place inside the sea
- Will help in forecasting Monsoon as it will measure parameters like ocean currents, temperature and salinity in the Arctic
- It will especially help scientist to move away from present Mathematical models for forecasting the Monsoon which many times vary from initial forecasts
India based Neutrino Observatory (INO)
The India-based Neutrino Observatory (INO) Project is a multi-institutional effort aimed at building a world-class underground laboratory with a rock cover of approx. 1200 m for non-accelerator based high energy and nuclear physics research in India
- Jointly effort by Department of Atomic Energy (DAE) & Department of Science & Technology (DST)
- Place > Bodi west hills, Theni district, South Tamilnadu
Key Features of INO
- Mega science project under 12th Five year plan, to setup an underground lab for pure science.
- Has 50,000 tones magnetic detector + an Iron Calorimeter detector to study neutrinos & particle physics
What are Neutrinos?
- Neutrinos are fundamental particles belonging to the lepton family.
- They come in three flavours, one associated with electrons and the others with their heavier cousins the muon and the Tau.
- According to standard model of particle physics, they are mass less.
- However recent experiments indicate that these charge-neutral fundamental particles have finite but small mass which is unknown.
- This was shown by observations of neutrino oscillation, which is a phenomenon by which one type of neutrino transforms into another.
Location factors of INO
- To detect Neutrinos and their reactions, the lab has to be at least 1000 m below surface, to reduce natural cosmic radiation
- Mountains of South India, are most ideal for this lab, because they’ve dense rock (mostly gneiss)
- Bodi west hills is made up of Charnockite (hardest rock known) hence Earthquake risk minimum
- One might wonder at the need for such a massive detector and for drilling underground.
- The reason is that the neutrinos interact very weakly with the surroundings.
- We are all being washed by a stream of neutrinos every passing minute as they just pass through us without leaving a trace.
- Since they interact so weakly, detecting them over other interactions is impossible.
- We need to have a barrier of at least 1 km of earth to keep itself away from all the trillions of neutrinos produced in the atmosphere and which would otherwise choke an over-the-ground neutrino detector. This is the reason scientists are now going underground.
Why Researching Neutrinos?
- Neutrinos are very important for our scientific progress and technological growth as they are abundant & have very feeble mass and no charge, which means they can travel through planets, stars, rocks and human bodies without any interaction.
- In fact, a beam of trillions of neutrinos can travel thousands of kilometres through a rock before an interaction with a single atom of the rock.
- They hide within them a vast pool of knowledge and could open up new vistas in the fields of astronomy and astrophysics, communication and even in medical imaging, through the detector spin-offs.
Terrestrial Observation and Predicting System (TOPS)
Ramakrishna Nemani, an Indian scientist in NASA has modified and adapted NASA technology to help Indian farmers against floods, droughts, climate change and smooth implementation of crop-insurance.
- TOPS system collects weather & climate data using remote sensing satellites, weather stations, climatic forecasting and ecosystem models
- This data helps in categorizing agro-regions according to climate risk, thus, crop production and loss can be determine in advance.
- Both farmer and Insurance companies can make ‘business’ decisions accordingly
- Ensures that right amount of crop insurance reaches the right farmer.
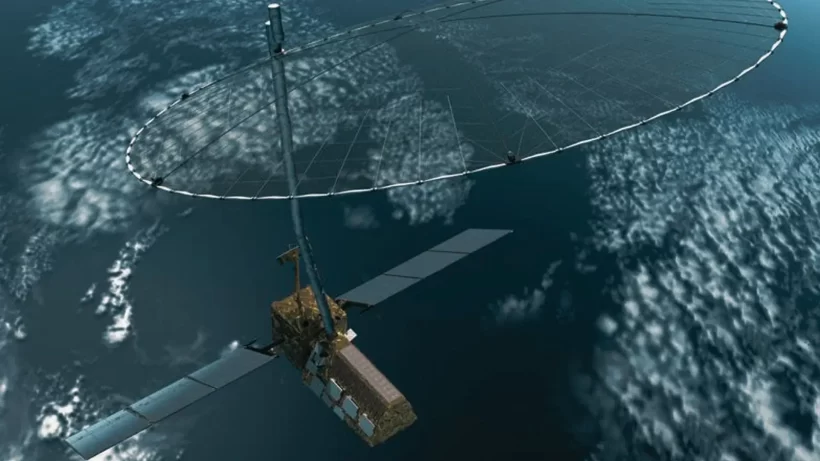
NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar Mission – NISAR
- Aimed to measure the changes on earth’s land surface, ice surface, glaciers, earthquakes and volcanoes & to find causes and consequences of such changes
- Will be launched by 2020 – NISAR will be the first satellite mission to use two different radar frequencies (L-band and S-band)
- Hence It will capture resolution even less than a centimeter of earth’s surface
- Preciseness required mainly to understand climate change & to predict natural disasters in advance
NASA to Provide
|
ISRO to Provide
|
For more updates, explore the Sci Tech. Feel free to share your thoughts and comments.
If you’re passionate about building a successful blogging website, check out this helpful guide at Coding Tag – How to Start a Successful Blog. It offers practical steps and expert tips to kickstart your blogging journey!