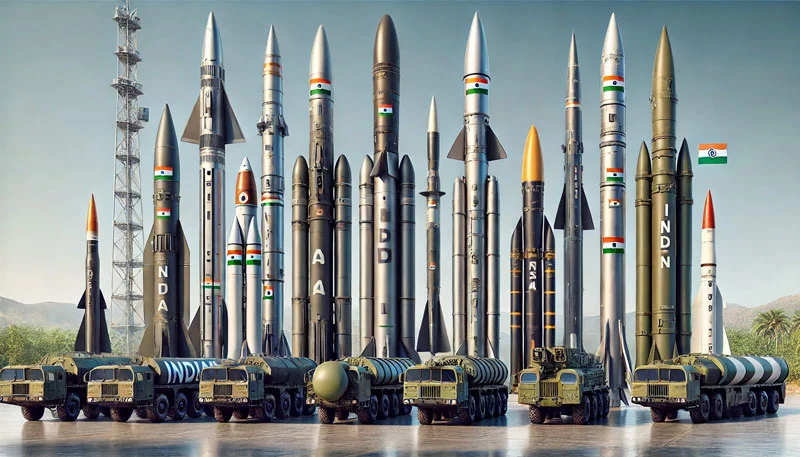
Missiles India
Ballistic Missiles
- Launched from land or sea; follows a trajectory with the objective of delivering one or more warheads to a predetermined target
- Usually carry a nuclear warhead and are very heavy & have much larger range
- Only guided during relatively brief periods of flight, and most of its trajectory is unpowered and governed by gravity (and air resistance if in the atmosphere)
- Long range intercontinental ballistic missiles are launched at a steep,sub-orbital flight trajectory and spend most of their flight out of the atmosphere
- Shorter range ballistic missiles stay within the Earth’s atmosphere
- Examples include Agni Missiles, Prithvi Missiles, Akash, Trishul, Maitri, Dhanush, Sagarika, K4, K5
Cruise missiles
- Can also be launched from air along with land and sea
- Have their own engines and wings to strike the target
- Can be sub-sonic (.8 mach), supersonic (3 mach) or hypersonic (5 mach)
- Highly accurate & fly within Earth’s atmosphere
- usually carry conventional warheads although some cruise missiles can also be equipped with nuclear warheads
- Examples include Brahmos Missiles, Nirbhay Missile
In both cases viz. Ballistic Missiles & Cruise Missiles are guided. That is, the flight path is pre-determined and very small alterations in flight are possible, if at all.
Ballistic Missiles India
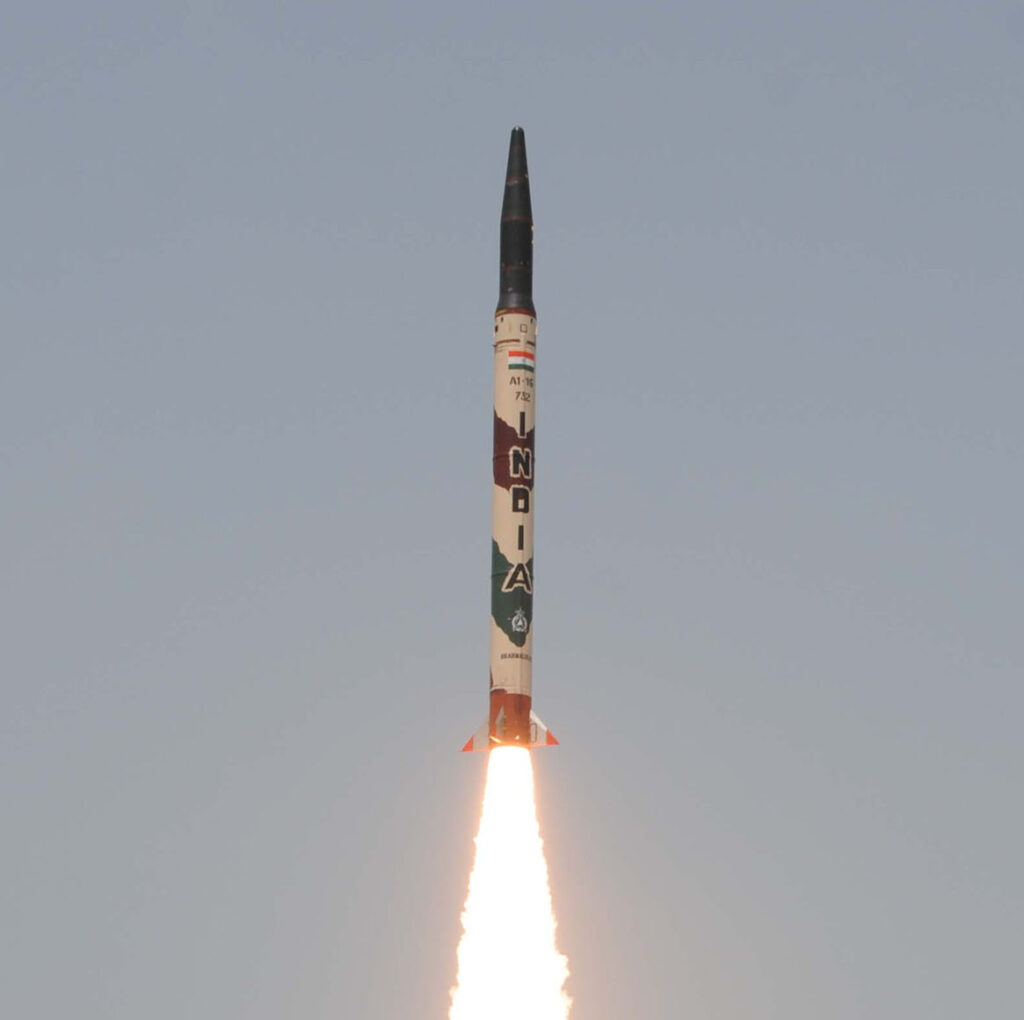
Agni Missiles
- Ballistic missiles carrying nuclear warheads
- Classified into three types viz. Medium Range Ballistic Missiles (MRBM), Intermediate Range Ballistic Missiles (IRBM) and Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles (ICBM)
| Name | Type | Range (Km) | Status | Type |
| Agni I | MRBM | 700-1200 | Deployed | Surface to surface |
| Agni II | IRBM | 2000-2500 | Deployed | Surface to surface |
| Agni III | IRBM | 3000-5000 | Deployed | Surface to surface |
| Agni IV | IRBM | 2500-3700 | Deployed | Surface to surface |
| Agni V | ICBM | 5000-8000 | Tested | Surface to surface |
| Agni VI | ICBM | 10000-12000 | Under Development | Surface to surface |
- Agni-I, Agni-II and Agni-III missiles were developed under the Integrated Guided Missile Development Program
- Agni IV + Agni V – high accuracy Ring Laser Gyro based Inertial Navigation System (RINS) and the most modern and accurate Micro Navigation System (MINS)
Prithvi Missiles
- Surface-to-surface short-range ballistic missiles (SRBM)
| Name | Range (Km) |
| Prithvi I | 150 |
| Prithvi II | 150-350 |
| Prithvi III | 350-650 |
- Dhanush is the naval variant of Prithvi Missiles – Sea to Surface
- Prithvi-II – 1st missile developed by DRDO under IGMDP
Prahaar
- A solid-fuelled Surface-to-surface Missile with range of 150 km
- Equipped with omnidirectional warheads and could be used for striking both tactical and strategic targets
India Sea Based Nuclear Armed Ballistic Missiles : Surface to Surface
- Submarine-launched ballistic missiles (SLBM)
| Name | Range (Km) |
| Dhanush | 350 |
| Sagarika (K15) | 700 |
| K4 | 3500 |
| K5 | 6000 |
Surface to Air Missiles of India
| Name | Feature | Range |
| Akash | surface-to-air | 30 km |
| Trishul | surface-to-air | 12 km |
| Maitri | surface-to-air | 15 km |
Akash Air Defence missile system
- Medium range Surface to air missile viz. approx. 35 km
- Can employ multiple air targets while operating in fully autonomous mode
- Can be launched from static or mobile platforms
- Can carry conventional and nuclear warheads
- Can operate in all weather conditions.
- Developed under the integrated guided-missile development programme by ISRO
LRSAM – India-Israel joint venture missile
- Long Range Surface to Air Missile (LRSAM) – called Barak 8 missile in Israel
- can take down an incoming missile as close as 500 meters away from the ship
Integrated Guided Missile Development Program (IGMDP)
- Prithvi Missiles – Short range surface-to-surface missile + Naval variant (Dhanush)
- Trishul Missiles – Short range low-level surface-to-air missile
- Akash Missiles – Medium range surface-to-air missile
- Nag Missiles – Third-generation anti-tank missile
- Agni Missiles – Only Agni 1, 2 & 3
Anti Tank Missile India
Nag Missile
- “Fire-and-forget” anti-tank missile
- An all-weather missile with a range of 3 to 7 km
- Uses Imaging Infra-Red (IIR) guidance with day and night capability
- Can be mounted on an infantry vehicle
A variant of NAG Missile to be launched from Helicopter is being developed under the Project named HELINA (HELIcopter launched NAg)
Cruise Missiles India
Brahmos Missiles
- can be launched from submarines, ships, aircraft or land (Cruise Missiles)
- Presently world’s fastest cruise missile in operation (Brahmos)
- Brahmos – Mach 2.8 Supersonic Cruise Missile developed in collaboration with Russia – 300 km
- Brahmos 11– Mach 7 Hypersonic Cruise Missile in development collaboration with Russia
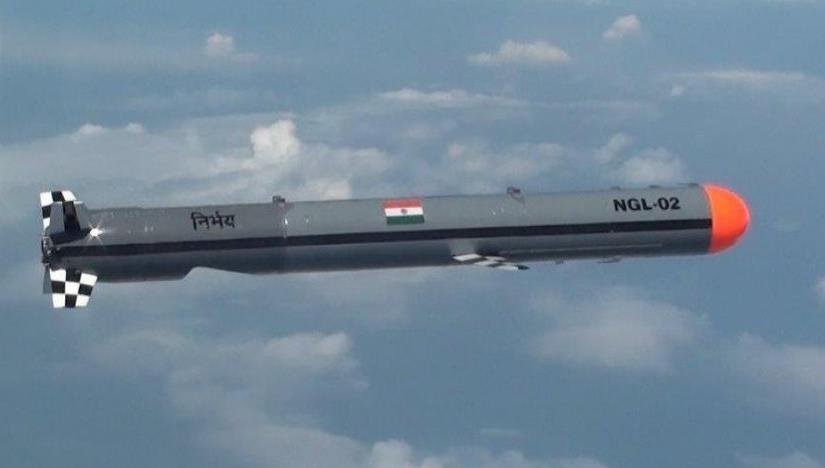
Nirbhay
- 1st long range subsonic cruise missile
- Can be launched from land, sea and air (Cruise missile)
- a ring laser gyroscope for high-accuracy navigation and a radio altimeter for the height determination
- Strike range – 1000 km
- From Integrated Test Range at Wheeler island, Chandipur, Orissa, by SFC monitored by DRDO
Air to Air Missile India
Astra Missile – India’s 1st Air to Air (BVR)
- Beyond Visual Range Air-to-Air Missile; smallest DRDO developed missile (3.8m)
- capable of engaging targets at varying range and altitudes allowing for engagement of both short-range targets (up to 20 km) and long-range targets (up to 80 km) using alternative propulsion modes
Unmanned Aerial Vehicle
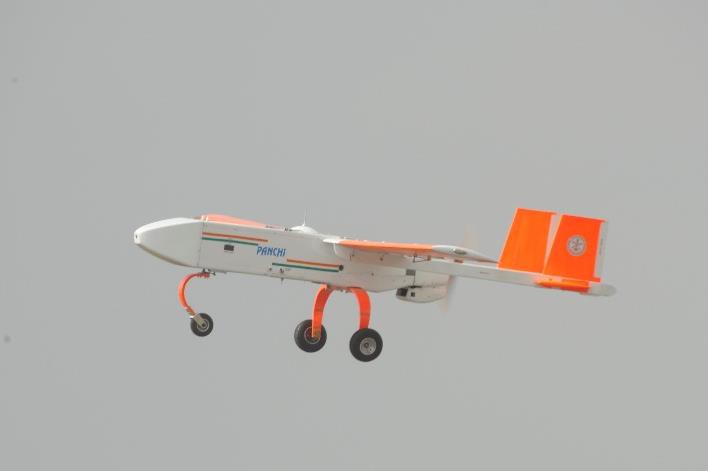
Panchi
- Wheeled version of Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) Nishant capable of taking-off and landing using small airstrips
- Have all the surveillance capabilities of UAV Nishant + longer endurance as it does not have to carry the air bags and parachute system as in the case of UAV Nishant
Nishant UAV
- a multi-mission UAV with Day/Night operational capability, inducted in Army
- designed for battlefield surveillance, target tracking & localization, and artillery fire correction
- controlled from a user friendly Ground Control Station + image processing system to analyze transmitted images from UAV
India’s Cold start Doctrine
- Though officially denied, it’s an offensive doctrine by the Indian strategic establishment
- Aimed at reducing mobilization time and improved network-centric warfare capabilities
Goal
- To establish the capacity to launch a retaliatory conventional strike against Pakistan that would inflict significant harm on the Pakistan Army before the international community could intercede
- At the same time, pursue narrow enough aims to deny Islamabad a justification to escalate the clash to the nuclear level
Offensive operations could begin within 48 hours after orders have been issued. Such a limited response time would enable Indian forces to surprise their Pakistani counterparts.
For more updates, explore the Sci Tech. Feel free to share your thoughts and comments.
If you’re passionate about building a successful blogging website, check out this helpful guide at Coding Tag – How to Start a Successful Blog. It offers practical steps and expert tips to kickstart your blogging journey!









2 comments
thanks sir
sir…….cau u plz upload test series with solution for prelims….