Issues related to Transgender
Transgender people are individuals of any age or sex whose appearance, personal characteristics, or behaviors differ from stereotypes about how men and women are ‘supposed’ to be. The main problems that are being faced by the transgender community are of discrimination, unemployment, depression, hormone pill abuse and problems related to marriage and adoption.
- Social stigma: since birth segregated from the society and lack social integration
- Education: lack access to formal schooling; further, lack of special schools for them.
- Employment: They represent less than 1% of total workforce.
- They are shunned by their own family.
- Politics and decision making processes have been out of their reach.
However, in recent times, transgender community has become more vocal about their rights. Even different organs of the government are trying to incorporate their issues and concerns.
In NALSA case (2014), Supreme Court held that transgenders should be treated as a ‘third gender’ for accessing public services. They will have right to self-identification of their gender as male, female or third-gender and are entitled to all the fundamental rights granted under the Constitution.
It also provided them with reservation in admissions to educational institutions as well as jobs.
- A ‘third gender’ option is now available in railway reservation forms, ration card applications, passport applications among other services
- Delhi government introduced “transgender category” in forms for registration of birth & death certificates.
- Allahabad HC – Transgenders would be treated as the “head of a household” under food security legislation
- Kerala – First state to have a policy for transgenders which aimed to end the societal stigma towards them
- Christian transgenders may get equal property rights soon
- Odisha became the first state which conferred the Below Poverty Line status to transgenders
However, one of the major issues they face is criminalizing of homosexuality under Section 377 of IPC. Although, Delhi High Court decriminalized homosexuality but it was overturned by Supreme Court in Koushal vs Naz Foundation case.
The Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Bill, 2016
- The Bill defines a transgender person as one who is (i) neither wholly female or male; (ii) a combination of female and male; or (iii) neither female nor male
- Protects transgenders from discrimination or denial of service in essential areas such as education, employment, healthcare, access to public places, goods and services
- Right of residence in the household – The person may be placed in a rehabilitation center on the orders of a competent court if the family is unable to care for the transgender person.
- Certificate of identity for a transgender person will be issued by the DM on request for conferral of rights
- measures to ensure the full inclusion and participation of transgenders in mainstream society via rehabilitation, vocational training, employment schemes etc.
- National Council for Transgender persons will be set up to advice the central government on the formulation and monitoring of policies
- Recognized offences – begging, forced or bonded labour, denial of use of a public place, physical, sexual, verbal, emotional and economic abuse, denial of residence in household or village
Critical Appraisal
- Eliminates the option of identification as either male or female
- Compulsory certification stands in violation of the self-identification principle
- Does not cover reservation provision as stated by SC in NALSA judgement
- Does not provide the definition of discrimination
“Gender equality in true sense can be achieved only if we incorporate all the genders in its definition”
For more updates about issues related to transgender, explore the Social Issues. Feel free to share your thoughts and comments.
If you’re passionate about building a successful blogging website, check out this helpful guide at Coding Tag – How to Start a Successful Blog. It offers practical steps and expert tips to kickstart your blogging journey!
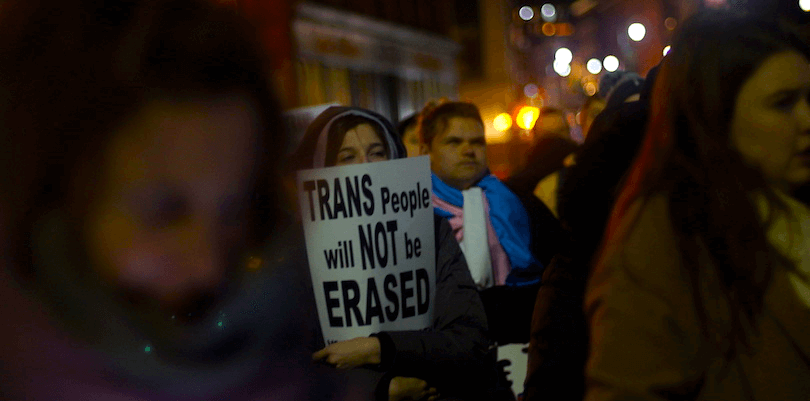





1 comment
very good effort