IRNSS, GAGAN, GSAT, ASTROSAT
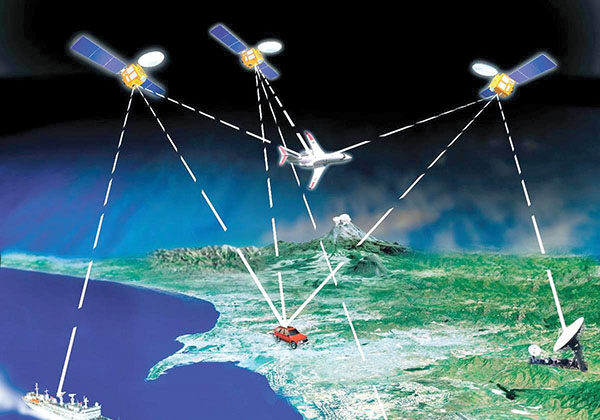
Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS)
- With an investment of 1420 Cr, 7 Satellites to be put in space by ISRO
- Will cover India + 1,500 km beyond its borders
- 3 satellites will be put in geostationary orbit + 4 satellites in pairs in two inclined geosynchronous orbits
- From the ground, these satellites will appear to travel in figures of ‘8’ during the course of a day
- Will be at a height of about 36,000 km, launched from Satish Dawan Space Centre in Sriharikota
- Will need a special receiver equipment to use navigation data, standard GPS receiver will not work
At present only two countries have fully functional global navigation systems
| USA | GPS – Global |
| Russia | GLONASS – Global |
| China | Beidou – Regional > Will be global by 2020 |
| Japan | Quasi-Zenith Satellite System |
| European Union | Galileo (GNSS) |
IRNSS Scientific principle
Microwaves
- Use two microwave frequency bands: L5 and S which travel at speed of light.
- Receiver will calculate the delay between microwave’s transmission & its reception, thus we get coordinates on earth.
Atomic Clocks
- For above microwave-calculation, Satellites have to periodically transmit their precise position in orbit with exact time, hence, they need to carry extremely accurate clocks with long shelf-life.
- Therefore, Each IRNSS satellite is equipped with rubidium atomic clocks, to keep precise time.
Services
- Will provide two kinds of services viz. Standard Positioning Services, available to all users, and an encrypted service, provided only to authorized users
- IRNSS System is expected to provide a position accuracy of better than 20 m in the primary service area
- To be able to use the IRNSS satellites, ISRO have to launch at least four of the seven planned IRNSS satellites
Global Positioning System Aided Geo Augmented Navigation System (GAGAN)
- A joint effort by the ISRO & Airports Authority Of India (AAI) for civil aviation purposes
- Aimed to help Air traffic control and helps pilots fly / land aircrafts in bad weather
- Depends on GPS (American navigation system)
India has become 4th nation after US, Europe & Japan to have inter-operable Satellite Based Augmentation System (SBAS) & 1st in the world to serve the equatorial region.
Working Pattern – GAGAN
- Works with the help of 3 Geostationary Satellites viz. GSAT-8, GSAT-10 and GSAT-15
- works by augmenting and relaying data from GPS satellites with the help of augmentation satellites and earth-based reference stations
- GAGAN system corrects any anomalies in the position data and gives accurate routes, landing guidance and time saving information to the pilots
- system would be available for the member states of the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC)
- It will be able to help pilots to navigate in the Indian airspace by an accuracy of 3 m
Major Benefits of GAGAN
- Improved efficiency,
- Direct routes
- Increased fuel savings
- Significant cost savings
Major drawback > only those aircraft that are fitted with satellite-based wide area augmentation system (SBAS) will be able to use the new technology
GSAT 16
- INSAT-3E is a communication satellite that powers DD & private TV channels, internet & radio signals.
- INSAT-3E is getting old and outdated, even stopped working in March 2014, after serving for almost a decade, hence need to be replaced with GSAT-16
- GSAT 16 is configured to carry a total of 48 communication transponders, the largest number of transponders carried by a communication satellite developed by ISRO so far
- The designed on-orbit operational life of GSAT-16 is 12 years.
- Placed in Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit at 55 degrees East longitude by European Ariane-5 launcher
GSAT 6
- It is aimed at primarily benefiting the country’s strategic and social applications
- Has life period of nine years & will povide S-band communication services in the country
- It includes a first-of-its-kind S-Band antenna with a diameter of six meter. This is the largest antenna ISRO has ever made for a satellite.
- It will offer a Satellite Digital Multimedia Broadcasting (S-band) service, via mobile phones and mobile video/audio receivers for vehicles.
ASTROSAT
- India’s 1st dedicated astronomy multi-wavelength satellite, aimed at studying distant celestial objects
- ASTROSAT will observe universe in the optical, Ultraviolet, low and high energy X-ray regions of the electromagnetic spectrum
- 1st mission to be operated as a space observatory by ISRO
Scientific objectives of ASTROSAT
- To understand high energy processes in binary star systems containing neutron stars and black holes
- Estimate magnetic fields of neutron stars
- Study star birth regions and high energy processes in star systems lying beyond our galaxy
- Detect new briefly bright X-ray sources in the sky
- Perform a limited deep field survey of the Universe in the Ultraviolet region
For more updates, explore the Sci Tech. Feel free to share your thoughts and comments.
If you’re passionate about building a successful blogging website, check out this helpful guide at Coding Tag – How to Start a Successful Blog. It offers practical steps and expert tips to kickstart your blogging journey!