India Roads, Railways, Ports & Airways
Road Transport >> 100 % FDI
National Highways
- Responsibility of National highway authority of India (NHAI)
- Constitutes 2 % of all roads & carry 40 % of total road traffic
- Funded by cess on petrol & high-speed diesel (From central road fund in public accounts of India)
- UP >> Highest length of National Highways
| NH7 | Varanasi – Cape – comrin (Kanyakumari) |
| NH6 | Surat – Kolkata |
| NH5 | Jharkhand – Chennai |
| NH2 | Delhi – Kolkata |
| NH8 | Delhi – Mumbai |
| NH4 | Mumbai – Chennai |
| NH3 | Agra – Mumbai |
International Border Highways
- Connects Indian borders with neighbouring countries.
- Responsibility lies with Border Road organization (BRO)
- Financed by World Bank
| NH1 | INDO – PAK BORDER (Delhi, Haryana, Punjab) |
| NH22 | INDO – CHINA BORDER (Haryana, Punjab, Himachal Pradesh) |
| NH35 | INDO – BANGLADESH BORDER (WB) |
| NH39 | INDO – BHUTAN BORDER (Assam, Nagaland, Manipur) |
| NH28A | INDO – NEPAL BORDER (Bihar) |
Famous Highway Projects
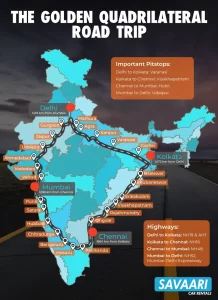
- Golden Quadrilateral >> 6 lane highway project connecting Delhi – Mumbai – Kolkata – Chennai
- North – South Corridor >> Linking Srinagar – Kanyakumari
- East – West Corridor >> Linking Silchar (Assam) – Porbandar
- Mumbai – Pune expressway (1st expressway of country) is not under NHAI as it was built by state government
State Highways
- Connects state capitals with district centres & are constructed by state governments
- Union from Central Road fund (CRF) provides grants & financial assistance to states, if required
- Maharashtra has the largest length of state highways
District Highways
- District centers to other important places of districts like business centers, industrial centers etc.
- Zila Parishad constructs & maintains these roads (Constitutes 1/3rd of total Indian roads)
- Maharashtra has the largest length of District highways
Village Roads
- Connects villages with neighboring towns & cities
- Responsibility of village roads lies with Gram Panchayat
- Central gov. has launched Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY) in 2000 as 100 % centrally sponsored scheme to provide rural connectivity to unconnected rural areas with population of 500 persons or more (250 persons in case of Hilly, Tribal & Desert areas)
Project Bharatmala
- A road built along India’s vast west-to east land border, approx. 5300km, from Gujarat to Mizoram
- Linking it to a road network in coastal states, from Maharashtra to Bengal
- This is a road network that will, as it were, garland the territory of India
- The Bharat Mala plan has a strong strategic component
- It’s India’s attempted answer to improve reach and connectivity in border areas, right across a large part of which lies China’s impressive road infrastructure
Rashtriya Rajmarg Zila Sanjoyokta Pariyojna – Roads will be developed to connect 100 district HQs across the country
Setubharatam – Govt to build 210 rails over bridges in the next two years and about 400-500 bridges would be built as standalone projects.
Indian Railways
- Mainly found in 3 gauges
- Broad Gauge = 1.675 m (70.72%)
- Meter Gauge = 1 m (92%)
- Narrow Gauge = .61 & .62 m (5.36%)
| Central Railways | Mumbai Central |
| Northern Railways | Baroda house, New Delhi |
| Eastern Railways | Kolkata |
| Western Railways | Mumbai Church Gate |
| Southern Railways | Chennai Central |
| North Central Railway | Allahabad |
| East Central Railway | Hajipur |
| West Central Railway | Jabalpur |
| South Central Railway | Secunderabad |
Metro Rails (Functioning)
- Kolkata (First mass rapid transit system in India)
- Delhi
- Bangalore (Wifi Enabled)
- Mumbai (Public Private Partnership)
- Jaipur
- Chennai
- Gurgaon (India’s first fully privately financed metro + India’s first fully privately financed metro stations)
Duronto Express >> Fastest Train in India (Called Restless in Bengali)
Diamond Quadrilateral >> High speed rails project connecting Delhi – Mumbai – Kolkata – Chennai
Dedicated Freight Corridor Projects |
||
| Amritsar-Kolakata | Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Bihar, Jharkhand & WB | Wholly by GOI, funded by WB |
| Mumbai Bengaluru | MH, Karnataka | Britain |
| Chennai-Bengaluru | Karnataka, TN, Andhra (Rayalaseema region) | JICA (Japan International cooperation Agency) |
| Delhi Mumbai (launched & Biggest) | UP, Delhi, Haryana, Rajasthan, Gujarat and Maharashtra. | |
Indian Ports
| Mumbai | Natural harbor & biggest port of India (Gateway of India)Handles approx. 1/5th of India’s foreign trade |
| Nava Seva | Jawalar Lal Port (Highly Mechanized Port) , Mumbai |
| Chennai | Oldest artificial harbor on east coast & 2nd largest port in terms of volume of traffic |
| Ennore | 1st corporate port (To release pressure on Chennai port) |
| Tuticorin (TN) | On Eastern coast of India |
| Kandla | Tidal Port (To release pressure on Mumbai port, developed after partition of India), Gujrat |
| Kochi | A natural harbor |
| Vishakhapatnam | Deepest artificial harbor on east coast |
| Kolkata | Riverine Port (Handles goods coming from SE Asian countries Australia & New Zealand) |
| Haldia | Developed on river Hooghly to relieve pressure on Kolkata port |
| Paradip | Located on Orissa coast |
| Mormugao | In Goa (5th in total traffic handled) |
| New Mangalore | On New Mangalore |
- Ennore – 1st corporate port (To release pressure on Chennai port)
- Indian Ports – 95 % by volume & 70 % by value – India’s international trade
- In monsoon, all western ports except Mumbai, Cochin & Kandila are closed (12 Major & 1 Minor Port)
- Maritime transport is to be administered by both the Central and the State governments.
- While the central government’s shipping ministry administers the major ports, the minor and intermediate ports are administered by the relevant state gov. of coastal states.
- All major ports, except one Ennore Port are government administered. It is the first port in India which is a public company.
Major Inland Waterways by Inland waterways authority of India (IWAI)
| Inland Waterway 1 | Allahabad-Haldia stretch of Ganga-Bhagirathi-Hooghly river system |
| Inland Waterway 2 | Sadiya-Dhubri stretch of the Brahmaputra River (Assam) |
| Inland Waterway 3 | Kottapuram-Kollam stretch of the West Coast Canal, Champakara Canal and Udyogmandal Canal (Kerala) |
| Inland Waterway 4 | Kakinada-Pondicherry along Godavari and Krishna River system |
| Inland Waterway 5 | Talcher – Paradip (Odisha) |
| Inland Waterway 6 | Lakhipur to Bhanga on the River Barak (Assam – Proposed) |
- Central Government has jurisdiction over both the National Highways and the National Waterways
- The States’ Governments have NO jurisdiction over the National Waterways.
- Indian Waterways à 1 % of total transport
- Length wise >> 1 > 4 > 2 > 5 > 3
- Inland waterways – 14500 km
- Indian coastline – Approx. 7500 km
River Interlinking Program India
The National Water Development Agency has already identified 14 links under the Himalayan Component and 16 under the one for Peninsular Rivers with priority to top 5 projects viz.
- Ken-Betwa
- Parbati-Kalisindh -Chambal
- Damanganga-Pinjal
- Par-Tapi-Narmada
- Godavari (Polavaram)-Krishna (Vijayawada)
The Himalayan Interlinking Rivers – 14

The Peninsular Interlinking Rivers – 16
Objectives of River Interlinking Project
- To diminish water scarcity in western and peninsular India
- To help in irrigation and storage as a large part of Indian agriculture is rainfall dependent
- To mitigate droughts and floods
- To reduce diversity between the water surplus and water scarce parts of India
- Will create employment
- Will help in socio – economic development of people
Opposition of River Interlinking Project
- Huge capital requirement
- Project may take 50 years to complete
- Can cause seismic hazards in Himalaya
- Execution is difficult as 21/30 links are dependent on other links
- Displacement of tribal and poor
- Interstate water disputes (political)
- Loss of forest and biodiversity
- International Conflicts with Nepal, Bangladesh
Project Sagarmala
- Project Sagarmala aims to improve India’s maritime infrastructure by modernizing existing major and minor ports of India and setting up new ports
- Prime objectives of Project Sagarmala
- to promote port-led direct and indirect development
- to provide infrastructure to transport goods to and from ports quickly, efficiently and cost-effectively
- The Sagarmala initiative will address challenges by focusing on three pillars of development, namely
- Supporting and enabling Port-led Development through appropriate policy and institutional interventions and providing for an institutional framework for ensuring inter-agency and ministries/departments/states’ collaboration for integrated development
- Port Infrastructure Enhancement, including modernization and setting up of new ports
- Efficient Evacuation to and from hinterland
- Under Project Sagarmala Shipping ministry has formed new Committee to setup two major ports
- Sagar, West Bengal
- Dugarajapatnam, Simandhra
- An illustrative list of the kind of development projects that could be undertaken in Sagarmala initiative are –
- Port-led industrialization
- Port based urbanization
- Port based and coastal tourism and recreational activities
- Short-sea shipping coastal shipping and Inland Waterways Transportation
- Ship building, ship repair and ship recycling
- Logistics parks, warehousing, maritime zones/services
- Integration with hinterland hubs
- Offshore storage, drilling platforms
- Specialization of ports in certain economic activities such as energy, containers, chemicals, coal, agro products, etc.
- Offshore Renewable Energy Projects with base ports for installations
Indian Airways
- Nationalized in 1953 – Indian Airlines
- Managed by Airport Authority of India (AAI)
GREEN INVESTMENT
|
BROWN INVESTMENT
|
For more updates, explore the Geography . Feel free to share your thoughts and comments.
If you’re passionate about building a successful blogging website, check out this helpful guide at Coding Tag – How to Start a Successful Blog. It offers practical steps and expert tips to kickstart your blogging journey!













8 comments
thankyou very much to share the knowledge.
Gatimaan express is the fastest train in India
Reading made easy
yours efforts are commendable and sincere thanks to you
Wow… amazing work… reading is made so simple
Your notes are so helpful! Thank you for this great endeavour, God bless
Really Useful. Many thanks Sir/Madam.
this is the most useful and admirable post which really helped me to solve my problem.
I have found so many useful link on your post page .
Where ever I look I found an useful post. I am really thankful to the Admin of this page.
I hope you will continue writing good quality post as you are writing now a days.
Best of luck.