Revenue Part of Indian Budget
Revenue [arr] Receipt [arr] Direct Taxes
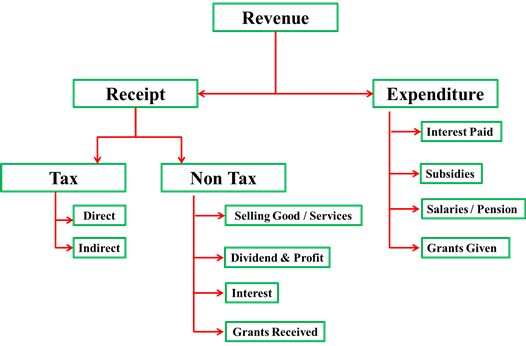
The Revenue Budget comprises revenue receipts and expenditure met from these revenues. The revenue receipts include both tax revenue (like income tax, excise duty) and non-tax revenue (like interest receipts, profits).
| On Income/ Expenditure | On properties/assets/Capital transaction |
|
|
Taxes marked in (*) have been abolished
Direct Tax Positives
- Progressive in nature viz. Richer person will pay higher tax
- Helps to reduce inequality of income
- Certain in nature viz. who to give, when to give & how to give
- Elastic in nature viz. quick results when they are raised or lowered
Direct Tax Negatives
- Collection expensive (staff salary, database Management) [arr] Narrow base
- Externality not counted [arr] Income earned by Tata (Production) vs Income earned by film star (Advertising)
- Hardship not counted [arr] Carpenter earning money vs landlord earning money
- High level of direct taxes –
- less tendency to work
- less foreign investment / foreign workers
- To encourage Savings & investment several tax deduction – exemptions given
| Direct Taxes of Union | Direct Taxes of States |
|
|
Income Tax slabs in Budget
| Taxable Income | Income Tax |
| 2.5 to 5 lakh | 10% |
| 5 to 10 | 20% |
| >10 | 30% |
- 3% education cess on income for all taxable income
- + 12% surcharge for income 1 crore or above: company or individual
| Surcharge | Cess |
| A kind of tax on tax (Only by central gov.) | A kind of tax on tax (Central + state both can) |
| Calculated only on tax liability | Calculated on tax liability + Surcharge. |
| For example, you have to pay 1 lakh as income tax & gov. demands 12% surcharge then total tax to be paid [arr] 1.12 lakh | Now education cess is 3 % then 3 % of 1.12 lakh will be counted [arr] Hence you will be paying Rs. 3360 in addition to 1.12 lakhs |
| Not taken for any specific purpose | Taken for a specific purpose viz. Education cess 2%, Secondary Higher Education cess 1%, Highway renovation, Mid-day meal |
| Goes to Consolidated Fund India | Goes to Public account of India |
| Finance Commission can’t share them with states (Not in divisible pool of taxes) | |
100% income tax deduction on donations towards
- Swatch Bharat Kosh managed by finance ministry
- Clean Ganga Fund managed by finance ministry trust
- National Fund for control of Drug Abuse managed by finance ministry
Other Direct Taxes of Union
| Corporate tax (Indian company) | ~30% (Will be decreased to 25 % till 2019) |
| Corporate tax (foreign company) | ~40% |
| MAT (Minimum alternative tax) | ~18.5% |
| STT Securities Transactions tax | 0.1%-0.25 % (Depending on nature of securities – future, option, equity etc.) |
Minimum Alternate Tax
To tax “zero tax companies” which in spite of having earned substantial book profits and having paid handsome dividends, do not pay any tax due to various tax concessions & incentives provided under Income-tax Law. Exemptions include –
- Infrastructure and power sectors companies
- Charitable activities
- Investments by venture capital companies
- Income arising from free trade zones.
Revenue [arr] Receipt [arr] Indirect Taxes
| Indirect taxes (Union) | Indirect Taxes (States) |
|
|
CST (Central sales tax) belongs to Union, but entire cash is given to States, hence, in budget estimates, its collection is listed as “–” or “00″.
Service Tax
- Custom act for custom duty + Excise act for excise duty
- No Service act for service tax but only a chapter in Finance Act 1994
- Article 268-A empowers union to collect service tax & share it with states in certain percentage
- Service tax is not applicable to service provider for < 10 lakh
| Service tax | 15.00% flat |
| Effective service tax | 15 % flat now [arr] 14 % + .5 Swatch + .5 Krishi |
Indirect Tax – Merits
- Convenient [arr] No additional paperwork for the customer
- Wider base [arr] Everyone is covered.
- Less evasion, especially under VAT / GST (Invoice credit)
- Highly Elastic [arr] Small increase brings large revenue
- Checks on harmful consumption via. Increasing indirect taxes viz. Cigar, alcohol, even for gold
Indirect Tax – Demerits
- Single point taxes [arr] High level of corruption, evasion, cascading effect e.g. sales tax
- Regressive in nature [arr] Both poor and rich taxed equally for the same item
- Poor people end up paying more portion of their income in indirect taxes.
Gross Tax revenue
- Total direct + indirect taxes of union + Total direct + indirect taxes of Union territories without legislature (All except Delhi & Pondicherry)
Net Tax revenue
- Gross tax revenue MINUS [revenue shared with states + money sent to National calamity contingency fund]
- Revenue to Country [arr] Direct Taxes >> Indirect Taxes
Revenue [arr] Receipt [arr] Non-Tax
- By providing goods and services [arr] (Other sources)
- All the money earned by Postal department.
- Police income: E.g., CISF giving security to Infosys, airport etc. They have to pay service fees to CISF.
- UPSC, SSC: their exam fees, RTI fees + fines
- when DRDO sells some technology/patent/product to other PSU or foreign government
- Money by Government Hospitals e.g. AIIMS
- when ISRO sells patent/technology/services to state governments, private companies, foreign governments/space agencies.
- Spectrum Auction=> Ministry of communication & Information Technology.
- India Year book, Yojana Magazine etc. [arr] Ministry of Information and broadcasting.
- By investment
- Government has shareholding in LIC, Coal India, SAIL, SBI etc. so these organization have to pay “Dividend” to Government (and to all other shareholders) [arr]If they sell such shares that’ll be disinvestment and fall under capital receipt part
- Interest received on loan given by Government to any PSU, State/UT/Foreign government
- Grant /Charity / Aid received by government of India
- All Non-Tax revenue collected by UT without legislature (All Except Delhi & Pondicherry)
- Maximum Revenue: Dividend > Others (selling goods / services) > Interest > External grant > UT
Revenue [arr] Expenditure
- Interest paid on the loans borrowed
- Subsidies (because they are short term/non-productive, hence under Revenue outgoing)
- Money paid to produce those goods/services
- Salary-pension-light bill telephone bill (including defense, CRPF etc.)
- Grants given to States/UT/Foreign countries
- Maximum Expenditure: Interest paid on loan > Subsidies > Defense > Pension > Grants
Revenue deficit [arr] Revenue Expenditure – Revenue Receipt
Effective Revenue deficit [arr] Revenue deficit – Grants given to State/UT for creation of capital assets.