Optics – Mirrors & Lenses
- Light follows a rectilinear propagation (3 * 108 m/s)
- Umbra > Point source of light > Shadow (Total dark)
- Penumbra > Extended source of light > Shadow (Partial dark)
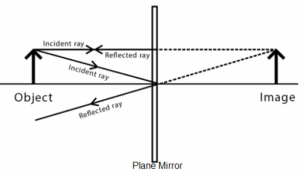
Plane Mirror
Angle of incidence (i) = Angle of reflection (r)
Image formed on Plane mirrors
- Virtual & Erect
- Equal distance & size
- laterally inverted
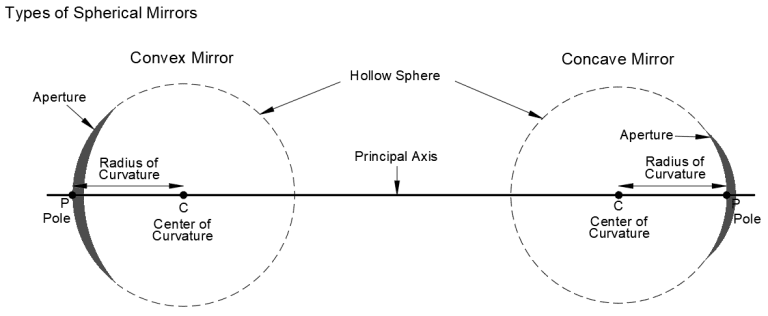
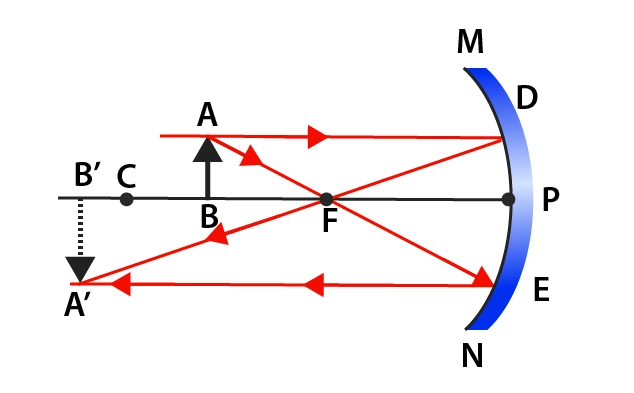
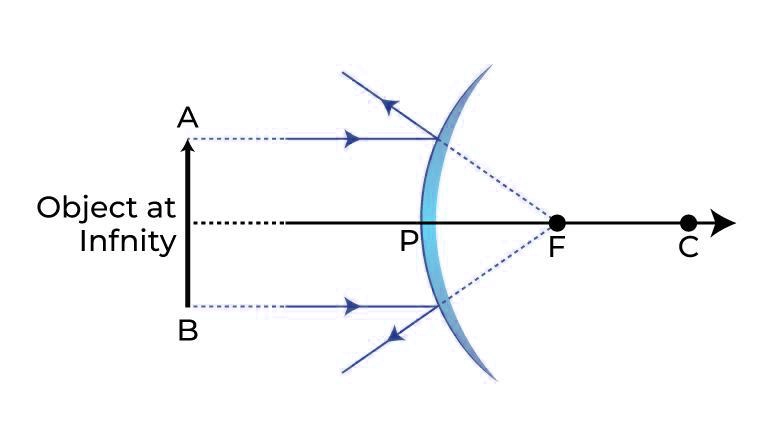
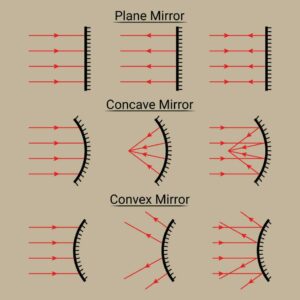
Concave & Convex Mirrors
Image formed by Concave Mirror
Image formed by Convex Mirror
Distinction between a Plane, Concave & Convex Mirror
Use of Concave & Convex Mirrors
| Concave Mirrors Torch,Vehicle headlightsShaving mirrors,Dentist MirrorConc. sunlight to produce heat | Convex mirrors Rear view mirrorsAlways gives erect though diminished imageProvides wider view |
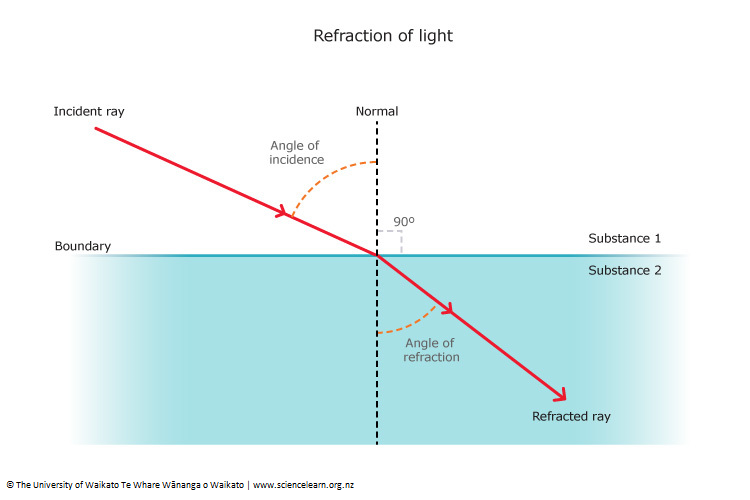
Refraction
- Velocity is higher in less denser medium
- n21 = v1/v2 (n21 > refractive index of medium 2 wrt medium 1)
- A ray of light will bend towards the normal if it is travelling from rarer to denser medium & away from the normal if it is travelling from denser to rarer medium
Few examples of refraction
- Twinkling of stars
- Sunrise & sunset (we can see the sun 2 min before the sunrise & 2 min after the sunset)
- Bottom of water filled body appears to be raised
Concave & Convex Lenses
|
|
|
Power of a lenses > Diopter |
|
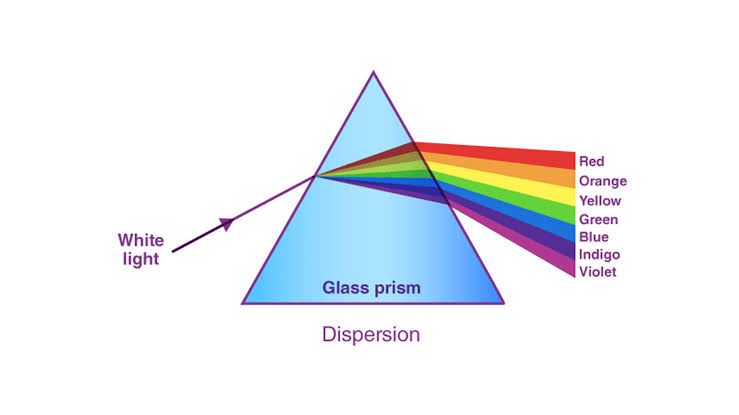
Dispersion of light
Total Internal Reflection
- Light can not always pass through denser to rarer medium
- if the angle of incidence > critical angle, it leads to total reflection of light
- Examples : Optical fiber, Mirage effect (Usually associated with hot deserts)
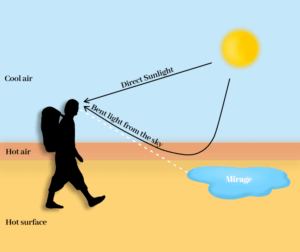
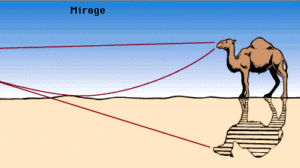
Mirage Effect
- Air near desert surface is hot & which cools rapidly with height (2 different mediums density wise)
- Rays from top of trees exceeds critical angle & TIR occurs
- Observer sees tree upside down giving illusion of water
- Vice a versa if air near the ground is cold & up above hot
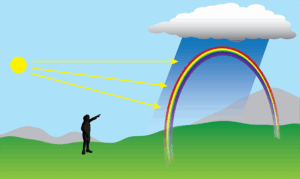
Rainbow
- Formed opposite of sun
- Process > Refraction & Dispersion + TIR + Refraction & Dispersion
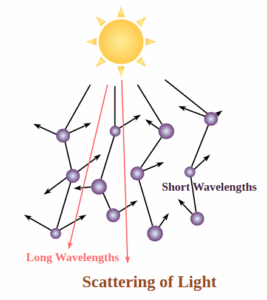
Scattering of Light
- A molecule of a medium emits incoming light in all possible directions known as scattering (Tyndall Effect)
Blue Color Sky
- When sunlight reaches earth’s atmosphere, Blue color scatters more strongly than the red
- When this scattered color enters our eye, sky looks blue to us
Reddish Sunrise / Sunset
- Light from sun near horizon passes through thicker layers of air & travel larger distances in earth’s atmosphere before reaching our eyes.
- Blue light & shorter wavelengths scatters away soon letting longer wavelengths of red light reach our eyes
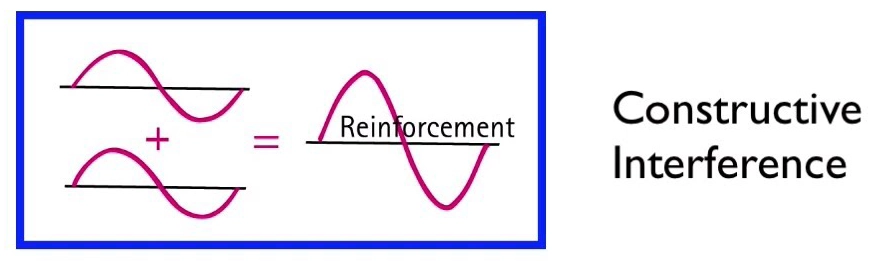
Interference of Waves
Superimposition of 2 waves of same kind which passes through same point at the same time
- Constructive interference – Same phase interference
- Destructive interference – Opposite phase interference
Example > Colors in soap bubble & oil on water in presence of white light (Alternate black & white spots in case of monochromatic light)
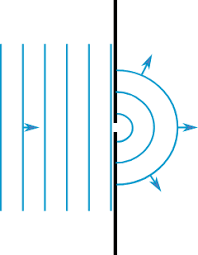
Diffraction
- Spreading of light through a narrow slit or aperture
- Failure of light to travel in a straight line (due to the wave nature of light)
Diffraction Grating > A device used to cause diffraction for ex. Parallel equidistant lines on glass or metals (as in CD)
Holograms > Result of Laser + Interference + Diffraction
✅ 10 Points – Importance of Optics: Mirrors & Lenses
-
Understanding image formation and vision correction.
-
Used in designing telescopes, microscopes, cameras.
-
Helps explain reflection, refraction, and total internal reflection.
-
Essential for optical instruments in medical fields.
-
Key in designing optical fiber communication systems.
-
Supports innovations in lasers and optical devices.
-
Important in understanding the working of eyes and vision defects.
-
Used in vehicle headlights, rearview mirrors, and magnifying glasses.
-
Basis for photography, filmmaking, and lighting.
-
Vital for research in astronomy and space exploration.
For more updates, explore the Physics. Feel free to share your thoughts and comments.
If you’re passionate about building a successful blogging website, check out this helpful guide at Coding Tag – How to Start a Successful Blog. It offers practical steps and expert tips to kickstart your blogging journey!