Mahajanapadas & Rise of Magadha
Mahajanapadas
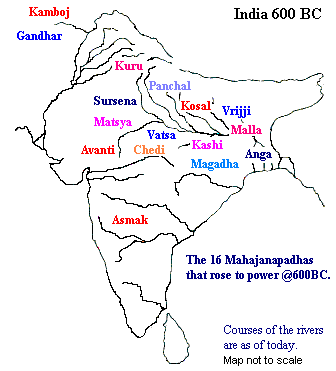
- Budhhist literature Angutara Nikaya gives a list of 16 great kingdoms or Mahajanapadas in the beginning of 6th century B.C
- Major reason of the formation of Janapadas was use of Iron tools for agricultural & military purposes
- In course of time small or weak kingdoms either submitted to stronger rulers or got eliminated. Finally in 6th century BC only 4 major kingdoms survived:
- Vatsa
- Avanti
- Magadha
- Kosala
Vatsa
- Shifted kuru clan with capital Kaushambi
- Most powerful ruler was Udayana
- After his death Vatsa was annexed to Avanti
Avanti
- Most important ruler was Pradyota
- Patronized Buddhism
- Finally, was annexed to Magadha
Kosala
- Most famous ruler was Prasenjit whose sister was married to Bimbisara
- Prasenjit gave Kasi as dowry to Magadha
- After his death Kosala became part of Magadha
Magadha
- Famous rulers were
- Most powerful kingdom of north India & founded by Jarasangha
- Bimbisara, Ajatashatru > (Haryankas)
- Shishunaga
- Nandas
Mahajanapadas |
Capital |
| Kamboja | Rajpura |
| Gandhar | Taxila |
| Surasena | Mathura |
| Matsya | Virat |
| Vatsa | Kaushambi |
| Chedis | Shuktimati |
| Kasi | Varanasi |
Mahajanapadas |
Capital |
| Avanti | Ujjain & Mahismati |
| Kuru | Hatinapur & Indraprastha |
| Panchala | Kampilya & Ahichattra |
| Kosala | Ayodhya & Sravasti |
| Mallas | Pava & Kusinagar |
| Vajjis | Vaishali |
| Anga | Champa |
| Magadha | Rajgir |
| Asmaka | Potana |
Rise of Magadha
Bimbisara (546 – 494 BC)
- Contemporary of both Buddhism & Jainism + Set up his capital at Rajgir (Known as Girivraja)
- Strengthened his position by marriage alliances (Kosala, lichhavi (Vaishali) & madra clan (Punjab))
- Acquired Anga under the viceroyality of Ajatashatru (Born of Lachhavi Princess)
- Fought with Pradyota of Avanti but later became friends
Ajatashatru
- Killed his father & succeeded to the throne
- Fought with Kosala & Vaishali (Lichhavis – destroyed it in 16 years) & won both war
- Embraced Buddhism & led the foundation for 1st Buddhist council at Rajgir
Udayin
- Successor of Ajatashatru + Founded new capital at Pataliputra
- His death marked the end of Haryanka dynasty.
Shishunagas
- Temporary shifted the capital to Vaishali
- Defeated Avanti & bought end to 100-year-old rivalry
- Transferred capital from Vaishali to Patliputra
Mahapadmananda
- Known as Ekarat (sole king who destroy others)
- Conquered Kalinga & bought image of Jina as trophy
- Hathigumpha inscription of Kharavela King (Kalinga) refers to conquest of Kalinga by Nandas
Dhanananda
- Last ruler of Nanda dynasty
- During his reign, Alexander invaded India but did not move ahead to east (Nanda’s Power)
- Chandragupta Maurya & Kautilya overthrew him as oppressive way of tax collection was already resented by people.
Cause of Magadha’s Success
- Advantageous geographical position & rich iron ores of Rajgir
- Capitals: Rajgir (Surrounded by 5 hills) + Patliputra (Surrounded by Ganga, Gandhak, Son & Ghagra river > True Jaladurga)
- Magadha > 1st used elephants in war against enemies.
Rise of Magadha – Factors Responsible:
Magadha, located in present-day Bihar, rose to prominence due to a combination of geographical, economic, political, and military factors.
1. Geographical Advantage:
-
Located in the fertile Gangetic plains, ideal for agriculture.
-
Surrounded by rivers like the Ganga, Son, and Champa, aiding trade, transport, and natural defense.
2. Rich Natural Resources:
-
Abundant iron ore in the Chotanagpur region enabled the production of superior weapons and tools.
-
Forests provided timber and elephants, crucial for warfare.
3. Strategic Location:
-
Situated near key trade routes and river systems, facilitating economic prosperity and troop movement.
4. Strong Rulers and Dynasties:
-
Capable leadership under dynasties like the Haryanka (Bimbisara, Ajatashatru), Shishunaga, and later the Nandas.
-
Bimbisara expanded Magadha through diplomacy and conquest.
-
Ajatashatru defeated Anga and the Vajji confederacy, further extending Magadha’s territory.
5. Military Strength and Innovations:
-
Magadha’s rulers maintained powerful standing armies.
-
Ajatashatru used innovations like the rathamusala (chariot with blades) and mahashilakantaka (catapults).
6. Political Expansion and Diplomacy:
-
Strategic marriages and alliances (e.g., Bimbisara’s matrimonial alliances with Kosala and Madra).
-
Systematic absorption of weaker Mahajanapadas through war or diplomacy.
7. Administrative Efficiency:
-
Organized bureaucracy helped maintain control over large territories.
-
Revenue from agriculture and trade funded the army and administration.
8. Decline of Rivals:
-
Weakened states like Kosala and Avanti eventually succumbed to Magadha’s growing power.
-
Republics like Vajji could not match Magadha’s centralized strength and resources.
For more updates, explore the IR & Security Category. Feel free to share your thoughts and comments
If you’re passionate about building a successful blogging website, check out this helpful guide at Coding Tag – How to Start a Successful Blog. It offers practical steps and expert tips to kickstart your blogging journey!







4 comments
and i think this not enough for upsc(IAS)
how to downlod this short note’
i need to downlopad this
Content is very good nd helpful