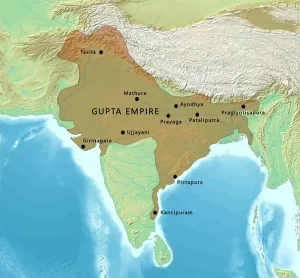
Gupta Empire (400 – 600 AD)
- On ruins of Kushan Empire rose Gupta Empire
- Constituted majority of UP & Bihar
- Main center of power at Prayag (Allahabad)
- Founder of Gupta Dynasty was Sri- Gupta
- Srigupta was succeeded by Ghatochkacha
- Both of them were called Maharaja
Chandragupta 1
- 1st to be called as Maharajadhiraja (Great king of kings)
- Married Lichchhavi princess which gave him strength & prestige.
- Considered to be founder of Gupta era as a mark of his ascension.
- Mehraulli iron pillar inscriptions mentions his extensive quests.
Samundragupta
- Known as greatest ruler of Gupta dynasty & Napolean of India
- Was opposite of Asoka & delighted in military conquest.
- Inscriptions of his military conquest are mentioned (in Sanskrit with Nagari script) on same Allahabad pillar which carries inscriptions of peace-loving Asoka.
- Samundragupta never knew any defeat & conquered east till Assam, west till eastern Afghanistan, North till Kashmir & south till Tamilnadu
- Was a lover of art & literature, Self-proficient in music & poetry, hence called Kaviraja
- Patronised many poets & scholars along with famous Harisena
- Was an ardent follower of Vaishnavism but tolerant to other religions
Chandragupta 2 (Chandragupta Vikramaditya)
- His reign saw high watermark of Gupta Empire
- Extended his empire by military conquests & marriage alliances
- Defeated Shakas in Malwa & Gujrat & conquered western seaport, henceforth, Ujjain became 2nd capital of Guptas, 1st being Prayag
- His exploits as Chandra has been mentioned on Qutub iron pillar Delhi.
- His reign at Ujjain court saw numerous scholars including “Kalidasa & Amarsimha”
- It was his reign under which Chinese pilgrimage Fa-hsien / Fahien (399-414 AD) visited India.
Fall of Gupta Empire
- Due to invasion of Hunas from central Asia
- Due to rise of Yashodharman in Malwa
- Due to dissention within the royal family & weak rulers
- The later Gupta’s embraced Buddhism while their predecessors were staunch Hindus.
Gupta’s Administration
- Unlike Mauryas, Guptas assumed titles like Parmeshwara, Maharajadhiraja & Paramabhattaraka
- Provinces in Gupta’s period were known as Bhuktis & provincial governors Uparikas
- King maintained close contacts with provincial administration through a class of officials called “Kumaramatyas” & “Ayuktas”
- Provinces were divided into districts Vishayas under charge of Vishayapati
- All foreign affairs were looked after by foreign affair minister known as “Sandivigraha”
- Villagers were subjected to forced labour called Vishti for serving royal army & officials
Religion & Social Culture
- Brahamans formed the top ladder & receive numerous gifts
- Brahamanism reigned supreme during Gupta period & had 2 branches mainly, Vaishnavism & Shaivism, with former more prevalent (Bhagavatism)
- Fahien accounts shows a decline of Buddhism in Gangetic valley but a few budhhist monks like Vasubandhu were patronised by Gupta kings
Art & Culture
- Gupta age is called golden age of India in field of art, science & literature.
- Nagara & Dravidian styles of art evolved during this period
- Delhi iron pillar, 7 ½ feet Buddha statue & Deogarh temple are finest example of Gupta art
- Mural paintings of Ajanta, which mainly depicted life stories of Buddha as in Jataka stories belong to this period (Paintings at Sigiria in Srilanka are influenced by Ajanta paintings)
Literature
- Sanskrit became primary language in Gupta period
- Ramayana & Mahabharata were compiled during this period
| Kalidasa | Abhigyanshakuntalam, Malvikagnimitram Vikramorvasiya, Kumarsambhava Raghuvamsa, Ritusamhara, Meghaduta |
| Vishakadatta | Mudrarakshash & Devi – Chandraguptam |
| Vishnusharma | Panchtantra stories |
| Sudraka | Mrich – chakatika (Little clay art or toy cart) |
| Amarsimha | Amarkosha (Lexicon in Sanskrit) |
| Dandin | Kavyadarsa & Desa – Kumarcharita |
Science & Technology
| Aryabhatta | Aryabhatiyam , Suryasidhhanta |
| Varahmitra | Panch Sidhhanta (5 astronomical system)Brihadsamhita, Brihadjataka (Astrology) |
| Vagbhata | Ashtangasamgraha (Summary of 8 branches of Medicine) |
Great Medical Trio of Ancient India > Charaka, Susruta & Vagbhata
🌟 Key Features of the Gupta Empire:
-
Major Rulers:
-
Chandragupta I – Founder of the empire.
-
Samudragupta – Known as the Napoleon of India.
-
Chandragupta II (Vikramaditya) – Peak of cultural and political expansion.
-
-
Administration:
-
Decentralized with local autonomy.
-
Efficient bureaucracy and land revenue system.
-
-
Economy:
-
Thriving agriculture and internal/external trade.
-
Use of gold coins (Dinaras), showcasing economic prosperity.
-
-
Art & Architecture:
-
Development of Ajanta caves, Buddhist stupas, and Hindu temples.
-
Introduction of Nalanda University for higher learning.
-
-
Science & Culture:
-
Aryabhata wrote the Aryabhatiya, explaining zero and astronomy.
-
Kalidasa, the greatest Sanskrit poet and playwright, wrote Abhijnanashakuntalam.
-
Advancements in mathematics, astronomy, medicine, and metallurgy.
-
-
Religion:
-
Flourishing of Hinduism, with tolerance for Buddhism and Jainism.
-
For more updates, explore the Ancient India History. Feel free to share your thoughts and comments.
If you’re passionate about building a successful blogging website, check out this helpful guide at Coding Tag – How to Start a Successful Blog. It offers practical steps and expert tips to kickstart your blogging journey!