Digital India
The National e-Governance Plan approved in 2006 has made a steady progress through Mission Mode Projects and Core ICT Infrastructure, but greater thrust is required to ensure effective progress in electronics manufacturing and e-Governance in the country.
Digital India aims to transform the country into a digitally empowered society and knowledge economy by leveraging IT as a growth engine of new India.
[clear]Vision of Digital India
Infrastructure as a Utility to Every Citizen
- High speed internet as a core utility
- Cradle to grave digital identity -unique, lifelong, online, authenticable
- Mobile phone & Bank account enabling participation in digital & financial space
- Easy access to a Common Service Centre
- Shareable private space on a public cloud
- Safe and secure Cyber-space
Governance & Services on Demand
- Seamlessly integrated across departments or jurisdictions
- Services available in real time from online & mobile platform
- All citizen entitlements to be available on the cloud
- Services digitally transformed for improving Ease of Doing Business
- Making financial transactions electronic & cashless
- Leveraging GIS for decision support systems & development
Digital Empowerment of Citizens
- Universal Digital Literacy
- Universally accessible digital resources
- All documents/ certificates to be available on cloud
- Availability of digital resources / services in Indian languages
- Collaborative digital platforms for participative governance
- Portability of all entitlements through cloud
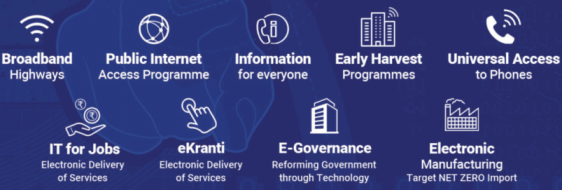
9 Pillars of Digital India
Broadband Highways
- Broadband for all Rural 250,000 GP by 2016
- Integration of SWAN, NKN, NOFN to be implemented in 2 years
Universal Access to Mobile Connectivity
- Remaining uncovered villages (~ 42,300 villages) by 2018
Public Internet Access Programme
- CSCs – made viable, multi-functional end-points for service delivery.
- Post Offices to become Multi-Service Centres
E-Governance: Reforming Government through Technology
- Government Business Process Re-engineering using IT to improve transactions
- Online applications and tracking, Interface between departments
- Use of online repositories e.g. school certificates, voter ID cards, etc.
- Integration of services and platforms – UIDAI, Payment Gateway, Mobile Platform, EDI
- Electronic Databases – all databases and information to be electronic, not manual
- Public Grievance Redressal – using IT to automate, respond, analyze data to identify and resolve persistent problems – largely process improvements
e-Kranti – Electronic Delivery of Services
- Technology for Education – e-Education
- Technology for Health – e-Healthcare
- Technology for Farmers
- Technology for Security
- Technology for Financial Inclusion
- Technology for Justice
Information for All
- Online Hosting of Information & documents
- Government pro-actively engages through social media
- 2-way communication between citizens and government
- Online messaging to citizens on special occasions/programs
Electronics Manufacturing
- Target NET ZERO Imports is a striking demonstration of intent
- Taxation, Incentives, Economies of Scale, Eliminate cost disadvantages
- Skill development + Government procurement
IT for Jobs
- Train people in smaller towns & villages for IT sector jobs
- Train Service Delivery Agents to run viable businesses delivering IT services
- IT/ITES in NE
Early Harvest Programmes
- Biometric attendance
- Wi-fi in All Universities
- Public wifi hotspots
- School Books to be eBooks
Impact of Digital India by 2019
- Broadband in 2.5 lakh villages, universal phone connectivity
- Net Zero Imports by 2020
- 400,000 Public Internet Access Points
- Wi-fi in 2.5 lakh schools, all universities; Public wi-fi hotspots for citizens
- Digital Inclusion: 1.7 Cr trained for IT, Telecom and Electronics Jobs
- Job creation: Direct 1.7 Cr. and Indirect at least 8.5 Cr.
- e-Governance & eServices: Across government
- India to be leader in IT use in services – health, education, banking
- Digitally empowered citizens – public cloud, internet access
Challenges
- Program on this scale never conceived
- Cyber-Security Issues
- Human Resource Issues
- Financial Resource Issues
- Coordination Issues