Capital Market – Equity
Points to Ponder in This Article – Understand the working mechanism of equity market, how it works, what are their pros & cons over and above bonds, what are IPOs & FPOs etc. Also read about the different investors which helps the new startups to fund and raise money.
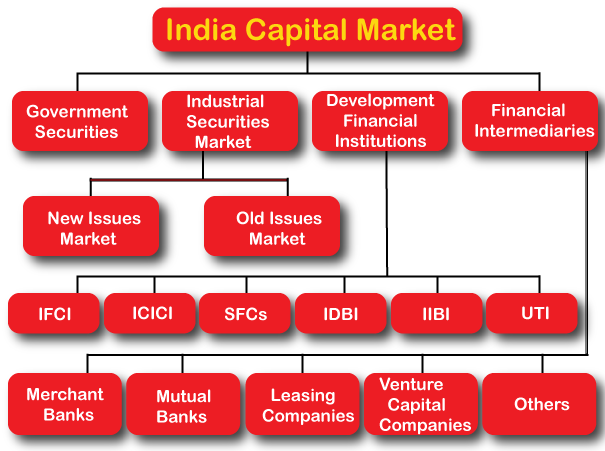
Financial Intermediaries > Regulate flow of cash b/w businesses & people / Economy & public.
Disintermediation > If these intermediaries are removed & companies raise money directly from public.
Money Market Miscellaneous Terms
Ways and Means Advances
- Government – temporary mismatch in receipt and payment
- RBI helps to fill mismatch fixes limit
- This mismatch is not counted under fiscal deficit
Misc. Debt Instruments
| T-Bills |
|
| Commercial Papers |
|
| Certificate of deposits |
|
Call money & Notice money
- Short-term borrowing among banks and FI
- No collateral required
- Mainly raised to fulfill CRR
- If raised for 1 day → Known as call money
- Over 1-day upto 14 days → Known as notice money
Difference between T Bills & G Securities
| T Bills | G Sec |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Zero coupon bonds > Without coupons bonds > Sold at a discounted price
Equities
- Company has to provide some % of shares out of its 100%
- Shareholders get dividend from profit
- Examples of Equity include IPO, Shares, Venture capital funds, Angel Investor fund
- Have last claim during liquidation of company
Securities: Debt vs Equity
| Debt (Bond) | Equity (Shares) |
|
|
Shares
- Shares provide ownership in the companies
- Under the Company law, one has to constitute a board of directors and hold annual general meeting of the shareholders.
- Board of Directors decides the dividend % of profit to the shareholders & investment of rest of the profit.
- For important policy decision, one will have to take votes of the shareholders
- One can become CEO of his own company & can withdraw an annual salary along with the dividend profit from the shares he hold
- An individual who owns 45 % share capital does not own 45% of that company’s assets. There is a difference between the sale of shares in a company and the sale of assets of that company.
Venture Capitalist
- A company that provides money, to start or expand your company but in return demand part of ownership
- Invest in big projects after studying their business plans & make an initial investment of US $ 250,000 to US $ 1.5 million.
- Venture Capitalist companies themselves borrow money from other companies like mutual funds, pension funds or may issue their own ‘bonds’to get money.
Angel Investors
- Rich gentlemen who finance startup companies for getting partial ownership and or assured returns on investment, after few years
- An Angel investor doesn’t mind taking huge risk by helping even small timers with totally unique and untested idea, if he think that it’ll grow up to huge success in future.
- Few examples financed by Angel investors > Amazon online shopping website and Starbucks coffee chain, Apple computers
Share versus stock
- Suppose a company has issued 1000 shares, worth Rs. 10 each & You paid Rs. 500 to purchase 50 shares of this company
- This means you own “50 Shares” of this company and “stock of Rs. 500” in this company.
- When we talk about shares we refer to the number of papers held by you
- When we talk about stocks, we refer to the money value of those papers held by you
Underwriter
- Formulates security papers to cover all the technically things, paperwork, SEBI regulations etc. for IPO / Bonds sales
- May offer an insurance of buying the IPO/Bonds if others don’t buy it e.g. Kotak Mahindra, ICICI
Also read: Capital Gains Tax, Transfer Pricing & GAAR
IPO vs FPO
| Initial public offerings (IPO) |
|
| Follow on public offerings (FPO) |
|
How IPOs are issued in Primary Market?
Promoter of Company
- Issue Red Herring prospectus to SEBI
- Red Herring prospectus contains all Business Info (promoters, directors, B plan) except Price & date of issue of shares
Underwriter
- Takes care of following work
- Printing of shares
- Allotment of shares
- Public issues of share
- IPO shares guarantee
- In US underwriters are known as Investment Bankers
- In UK underwriters are known as Merchant Bankers
IPO Value Calculation
Fixed pricing Method 1 lakh equity shares to be issued in market
|
Book Building Method
|
Bonus Shares
- When company provides extra shares to shareholders instead of dividend in a specific year at no extra cost
- Means company paid the money to purchase shares on your behalf
Employee stock option scheme
- Company issues shares to its employee at a discount price to make the employees committed to the success of company
- If the company makes more profit, they can walk away with higher dividends.
- Generally such shares have minimum lock in period of one or two years
Rights Issue
- Existing shareholders given first right to purchase new shares according to their existing shareholding
- If they refuse > offer to common public
- Not applicable to IPO but on FPO
Issuing additional shares after IPO to raise more money for business, but under the companies act, you can issue additional shares to the existing shareholders only. This is called “rights issue of shares” (Generally at discounted rates to shareholders) – Mainly done to raise more money & reduce debt to equity ratio
Debt Equity ratio
- Credit rating agency look into a company’s performance, assets, liability everything & one of the thing they’re most interested in, is “Debt to Equity” Ratio
- More “Debt to Equity” Ratio lower the rating provided by these agencies
Share splitting
- Presently 1 share x Rs. 1000 face value
- After share splitting 100 share x Rs. 10 face value
- Provide liquidity to investor viz. can easily sell Rs. 10 share than Rs. 1000 share
- Increases retail participation
- Doesn’t increase company’s market capitalization or its value
Central Public Sector Enterprises – Exchange Traded Funds (CPSE –ETF)
- Type of disinvestment, in which government’s shares are being sold to private players lets say Goldman Sach
- Goldman Sach put these shares on sale at stock exchange so, that general public can buy it.
- Minimum order has to be Rs. 5000
- First time investor (whose annual income is below Rs. 12 lakh) will get tax benefit under Rajiv Gandhi Equity Savings Scheme (Up to Rs. 50k)
Rajiv Gandhi Equity Savings Scheme (RGESS)
- New tax saving scheme, announced in Budget 2012 which aims to attract more (middle class and lower middle class) people to invest in securities market
- Mainly to divert them from investing money in gold, which increases current account deficit and creates more problems for Indian economy
| Conditions | Benefits |
|
|
Derivatives
- Which derive value from assets viz.
- Physical Assets (Home, Office, Machinery)
- Debt / equity
- Forex
- Commodity
- Derivatives Future / forward contracts > Sell / Purchase / Execution of order at future date
- Derivative options > To minimize risk on future/forward contracts
- Call option > Right to buy, but no obligation to buy
- Put option > Right to sell, but no obligation to sell
Some terminologies associated with equity market
| Free float market cap (FFMC) | Price of each share x total number of shares with public |
| Stag investor | One who buys IPOs to resell it in future |
| Bull investor | Hopes that prices will rise, hence purchase more of shares |
| Bear investor | Fears that prices will fall, hence sells more of shares |
| Sensex | Weighted average of FFMC of top 30 companies of BSE |
| Nifty | Weighted average of FFMC of top 50 companies of NSE |
Share market position
- Down in situations of War, Inflation & political instability
- UP in case of soft monetary policy, relaxing FDI norms, M & A rumors
Problems with Paper shares
- Delivery problem.
- Fear of theft
- Transfer delay
Solution > Dematerialization
- A person can open up a Demat account with the help of Pan card, Bank account & Address proof
- Depositary participants like SBI, HDFC, ICICI etc. provide you an online platform to buy / sell shares electronically
- Net shares bought /sold are kept with the depositary participants in paper format
- Depositary participant emails the record of net shares bought / sold to NSDL or CSDL
- NSDL or CSDL then issues shares in electronic format to depositary participants
- NSDL > National Securities Depository Limited > Deals with National Stock Exchange (NSE)
- CSDL > Central Depository Services Limited > Deals with Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE)
- They are electronic depositories to hold all the securities electronically in de-materialised format









1 comment
sir please correct the mistake in difference between equity and debt