Volcanoes & its types
Volcanoes
- A sudden & abrupt explosion in earth crust through which Magma, gases, dust, smoke & solid material burst out
- Volcanic activity is connected with crustal disturbances, closely related with regions that have been intensely folded or faulted
- Magma while thrusting its way up to the surface may cool & solidify within crust as Plutonic rocks resulting in intrusive landforms.
- Magmas that reach the surface & solidify, form extrusive landforms
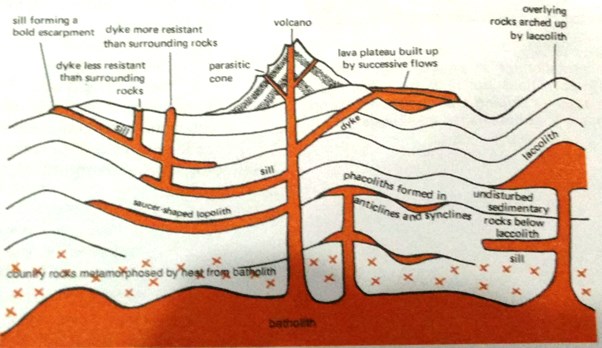
Sills & Dikes (Common Intrusive landforms)
- When an intrusion of molten magma is made horizontally along the bedding planes of sedimentary rocks, the resultant intrusion is called a Sill.
- Similar intrusion when injected vertically as narrow walls of igneous rocks within the sedimentary layers are termed as Dikes.
Igneous intrusions on a larger scale are various types of Liths viz. Laccoliths, Lopoliths, Phacoliths & Batholiths
| Laccoliths | An igneous mound with a dome shaped upper surface & a level base, fed by a pipe like conduit from below |
| Lopolith | An igneous intrusion with a saucer shape |
| Phacolith | A lens shaped mass of igneous rock occupying the crest of an anticline or the bottom of a syncline & being fed by a conduit from beneath |
| Batholith | A large emplacement of igneous intrusive rock, mainly granite, that forms from cooled magma deep in the Earth’s crust |
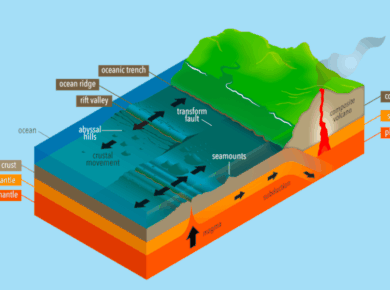
Extrusive Landforms
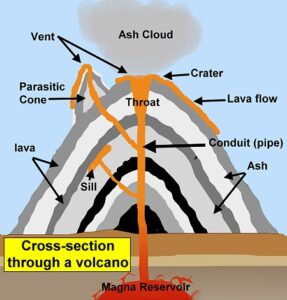
- Lava or molten magma ejects at a very high pressure through a pipe known as Volcano’s neck or vent
- Top portion of volcano is known as crater and a crater lake is formed when rain water gets accumulated in
- Some volcanos may have greatly enlarged depressions like cauldron known as Calderas
- Volcanic dust or ash (finer particles) that emerges out of volcano travels round the world & falls as black snow, which can bury house & people.
- The coarser fragmental rocks are collectively called as Pyroclasts which include cinders, pumice & volcanic bombs.
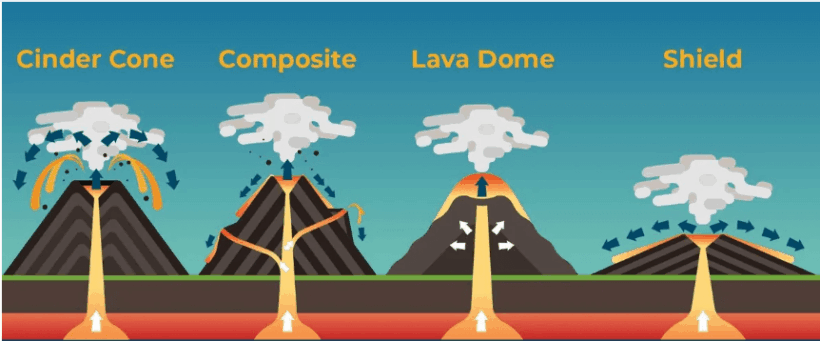
Types of Volcanoes
Active Volcano
- Keeps on ejecting volcanic material at frequent intervals
- Ex – Etna (Italy), Stromboli (Sicily-largest Island in the Mediterranean Sea, near Italy)
- Mt Stromboli > Lighthouse of the Mediterranean
Dormant Volcano
- One in which eruption has not occurred for a long time but can occur any time in future
- Barren Island (Andaman), Versuris (Italy)
Extinct Volcano
- No eruption has occurred in historic times & possibility of future eruption is also remote
- Mt. Popa (Myanmar). But we can never be thoroughly sure about them.
- Vesuvius (Bay of Naples near Italy) & Mt. Krakatau (Sunda straits b/w Java & Sumatra) were thought to be extinct & yet both erupted violently
Distribution of Volcanoes in the world
-
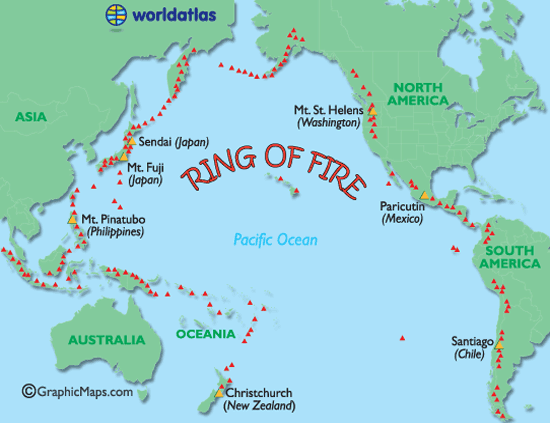
- There are mainly three volcanic belts, besides many volcanoes which are outside these belts.
- Circum-Pacific belt > known as Ring of fire & houses around 2/3rd of world’s Volcanoes.
- Mid-Continental belt > This belt has various volcanoes of the Alpine Mountain chain, Mediterranean Sea (Stromboli, Vesuvius, Etna etc.)
- Mid-Atlantic belt > This belt includes the volcanoes of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge
Geysers
-
- A spring characterized by intermittent discharge of water ejected turbulently and accompanied by steam
- The phenomenon is associated with a volcanic region in which the water below is being heated beyond its boiling point
- Is often triggered off by the gases seeping out of the heated rocks.
- Examples include Iceland, New Zealand & Yellowstone Park of USA
- The world’s best known geyser is perhaps old faithful in Yellowstone National park, Wyoming
Hot springs
- A spring that is produced by the emergence of geothermal heated groundwater from the Earth crust
- Is more common than geysers
- The water rises to surface without any explosion
- Such springs contain dissolved minerals which may be of medical value
- Examples Include Iceland, Japan & Hawaii
For more updates, explore the Geography . Feel free to share your thoughts and comments.
If you’re passionate about building a successful blogging website, check out this helpful guide at Coding Tag – How to Start a Successful Blog. It offers practical steps and expert tips to kickstart your blogging journey!






1 comment
thankyou very much to share the knowledge.