The Great Depression of 1929
The worldwide economic crisis which began in 1929 originated in USA. The years after the First World War saw a big increase in production of goods in America. In spite of this, however, more than half of the population lived at less than the minimum subsistence level.
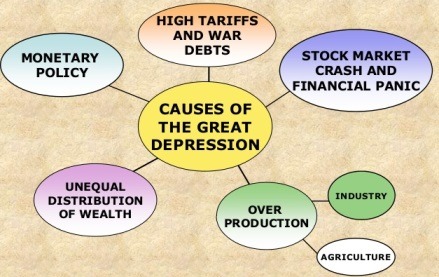
- As capitalist tried to maximize their profits by producing more & more goods, a crisis was caused by the overproduction.
- Production increased but the purchasing power of the workers remained low, & the goods could not be sold unless their prices are reduced.
- However, the prices could not be reduced because this would affect the profits.
- So, the goods remained unsold, and the factories were closed to stop further production.
- With the closure of factories people were thrown out of employment which made the situation worse.
- Such crises occurred often in almost every country after the spread of the Industrial Revolution.
- The crisis of 1929 – 33 was, however, was the worst in history.
- In October 1929, the entire economy began to collapse.
- The stock market in New York Crashed.
- The fall in the value of shares created so much panic that in one day 16 million shares were sold in NY Stock Exchange.
- In some companies, the shares held by people became totally worthless.
- During the next four years, more than 9,000 American banks closed down and millions of people lost their life’s savings.
- The manufacturers and farmers could not get any money to invest.
- People had little money to buy, hence the goods could not be sold.
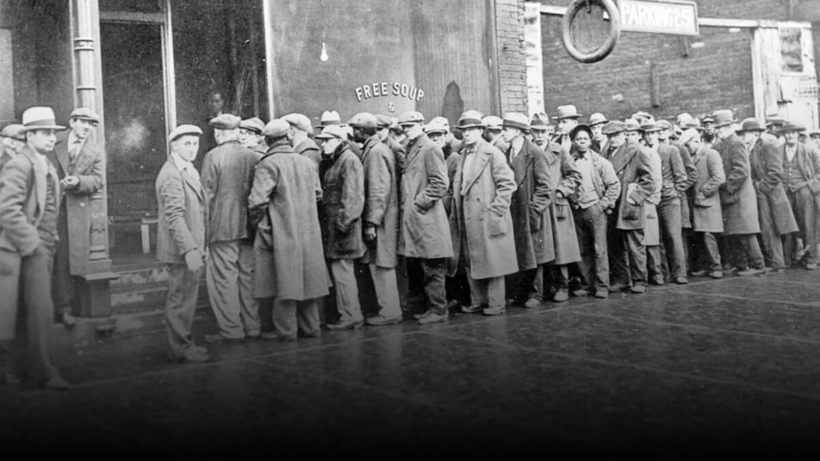
- This led to the closing of thousands of factories and throwing of workers out of employment.
- The purchasing power of the people was thus further reduced which led to the closing down of more factories and to more unemployment.
Spread of Depression to Europe
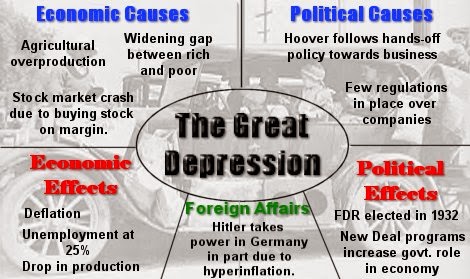
The Depression began to spread to all the capitalist countries of Europe in 1931. After the First World War, the economies of the countries of Europe, excluding Russia, had become closely connected with and even dependent on the economy of USA, particularly on the American banks. The consequences of the Depression in Europe were similar to those in the USA and in some cases even worse.
- The Depression resulted in large scale unemployment, loss of production, poverty and starvation.
- It continued throughout the 1930s, even though after 1933, economies of the affected countries began to recover.
- The crisis as long as it lasted was the most terrible &affected the lives of scores of millions of people all over the world.
- Thousands of factories, banks and business enterprises stopped working.
- The industrial production fell by about 35 per cent, in some countries by about half.
Impact of the Great Depression
- The economic crisis had serious political consequences.
- Nazis in Germany exploited the discontent of the people to promote their anti-democratic programme.
- In many countries, hunger marches were organized, and the socialist movement pressed for far-reaching changes in the economic system.
- The only country which was not affected by the economic crisis of 1929-33 was USSR.
- The economic crisis worst affected—the economy of the United States. It led to the victory of the Democratic Party and Franklin D. Roosevelt became the President of the United States in 1933.
- Under his leadership a programme of economic reconstruction and social welfare was started.
- This programme is known as the New Deal.
- Steps were taken to improve the conditions of workers and to create employment.
- As a result of the New Deal, the economy of the United States recovered from the crisis and the industrial production picked up again.
The United States had retained her position as a mighty power. However, her foreign policy was not very different from that of Britain and France.
It, like Britain and France, did not adopt a strong position to resist aggressive acts of fascist powers until after the outbreak of the Second World War.











1 comment
thankyou very much to share the knowledge.