India ASEAN Relations
India adopted the “Look East Policy” soon after economic liberalisation in 1991 to increase economic & commercial ties with East and Southeast Asian.
- ASEAN India Free Trade Agreement – An essential step towards deeper economic integration
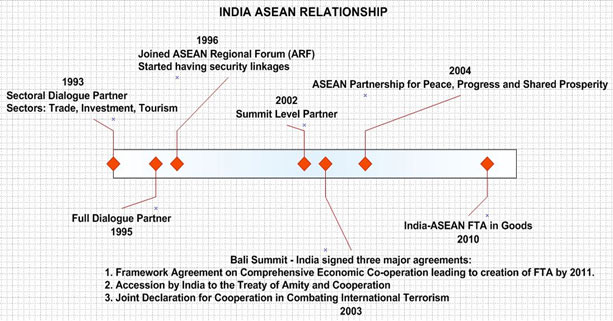
- India was accorded full ASEAN Dialogue Partner Status in 1995, followed by its membership in ASEAN Regional Forum. ASEAN has been a strategic partner of India since 2012.
- Commerce, Culture and Connectivity are the three pillars of India’s robust engagement with ASEAN.
- Under the AEP, India not only expected to bolster its economic engagements with the region; it yearned to emerge as a potential security balancer as well.
India has attempted to demonstrate its ability to play a dynamic role in the region. India sent a strong signal to China by mentioning the importance of maintaining freedom of navigation in the South China Sea, respecting United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS)
[clear]ASEAN Significance
- ASEAN countries, particularly Myanmar, Vietnam & Malaysia can potentially contribute to India’s energy security.
- The highly underdeveloped NE States of India, which lie at the gateway to a region offering unlimited economic opportunities, will witness an economic transformation.
- Trade between India and ASEAN comprises 10.12% of India’s total trade with the world
- Conclusion of a balanced Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) Agreement will further boost our trade and investment ties with the region.
- Cooperation in areas such as maritime security including freedom of navigation, drug trafficking and cybercrime
‘Act East’ Policy
- India’s ‘Act East’ policy, upgraded from ‘Look East’ policy in 2014, serves as a platform for deepening and strengthening its economic, cultural & strategic relationship with ASEAN and the East Asian economies.
- Providing enhanced connectivity to North East states of India ASEAN and the East Asian economies, has been a priority in Act East Policy.
India has pushed a host of trans-national projects that seek to weave the region together:
- India has set up an Indian mission to the ASEAN in Jakarta, and has set up an ASEAN-India Centre which is housed in New Delhi.
- Kaladan Multi-Modal Transit Transport Project will connect Myanmar to NE India
- Tamu-Kalewa-Kalemyo sector of the India- Myanmar-Thailand Trilateral Highway is a work in progress and is expected to create a new dynamic in India’s multi-faceted ties with the region.
- India is also set to launch a Tracking & Data Reception Centre in Vietnam, which would make remote sensing data available from Indian Satellites for applications in disaster management and mineral exploration for ASEAN countries.
- ASEAN-India Agreement on Trade in Service and Investments has entered into force for India and seven ASEAN countries
From Look East to Act east
The transformation from “Look East Policy” to Act East Policy is not merely of terminology. The AEP has gone way far and wider than the Look East Policy –
- AEP has imparted greater vigour to India’s ties with ASEAN. Relations, which were stagnating, are again assuming renewed vitality.
- India has now recognized that the success of AEP will be determined by its contribution to security and economic development of Northeast India. And thus, many efforts have been in the direction.
- Relations with ASEAN now encompass security, strategic, political, counterterrorism, & defence collaboration in addition to economic ties.
- The policy has sought to significantly expand its geographical coverage beyond ASEAN, to include other countries like Japan, Australia, Pacific Island nations, South Korea, and Mongolia.
- Government has also sought to rejuvenate ties with countries that have been neglected in recent years, including Australia, Fiji and Mongolia.
With ‘Make in India’ emerging as a key campaign for manufacturing, developing new global value chains in partnership with the economies of ASEAN would bring benefits to both sides. India is also expected to play a significant role in upholding the security and stability of the region, which India needs to get ready for.