Plant Classification & Parts of Tree
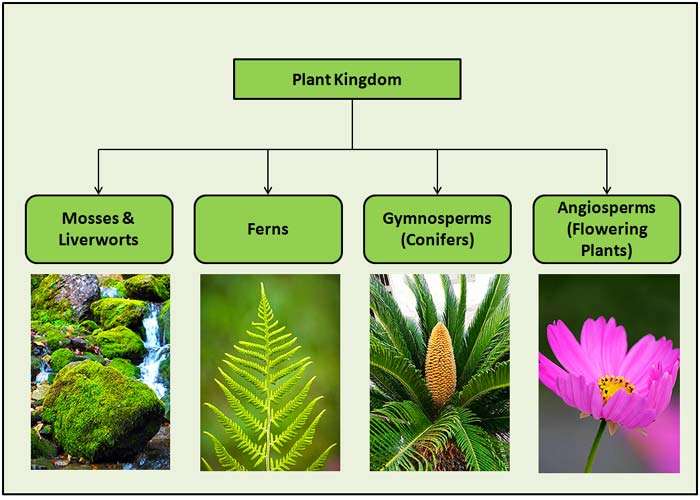
The Classification Of Plants is mainly based on the plant Taxonomy, life cycle, flowering, non-flowering, and the number of seeds.
Herb
- A plant whose stem is always green & tender
- Height not more than 1 meter
- Banana plant is the world’s largest herb
Shrub
- A woody plant, smaller than a tree, & of max height 6 meters
- Has several main stems arising at or near the ground
Tree
- A woody perennial plant, typically having a single stem or trunk growing to a considerable height
- Bearing lateral branches at some distance from the ground
Parasite
- An organism which lives in or on another organism (its host) and benefits by deriving nutrients at the other’s expense.
- They penetrate their roots (Haustoria) into the host plant to derive minerals, moisture & nourishment.
Epiphyte
A plant that grows non-parasitically upon another plant (such as a tree), and derives its moisture and nutrients from the air, rain, and sometimes from debris accumulating around it instead of the structure it is fastened to.
- Normally grows on another plant for support.
- It is not parasitic in nature & uses the host plant for support only
- Found commonly in tropical rain forests
Climbers
- Plants which grow upright, relying on other plants, rocks and manmade structures, and anything else they can find for support
- Example → Vine plant
Parts of a tree
Roots
- Convey water and nutrients from the soil to the rest of the plant via numerous branches and fibers.
Crown
- Made up of the leaves & branches at the top of the tree.
- The crown shades the roots, collects energy from the sun (Photosynthesis) & allows the tree to remove excess of water to keep it cool via transpiration

Leaves
- A usually green, flattened, lateral structure attached to a stem and functioning as a principal organ of photosynthesis and transpiration in most plants, also known as food factory of the plant
- converts energy into food (sugar) as they contain chlorophyll, which gives green color to the leaves & allows plants to absorb energy from light i.e. convert carbon dioxide & water into carbohydrates
- Light energy is absorbed by chlorophyll, while air containing carbon dioxide and oxygen enters the plant through the leaf stomata.
Photosynthesis Reaction > CO2 + H2O + Sunlight >>>> Glucose (Sugar) + Oxygen
Branches
- Arms of the tree, a woody structural member connected to but not part of the central trunk of a tree
- Provide the support to distribute the leaves efficiently & serves as a conduit for water & nutrient and as storage for extra sugar
Trunk
- Provides shape & support to the tree & holds up the crown
- Supplies water & nutrients from the soil & sugars from the leaves via its branches.
Parts of the Trunk of a Tree
Annual Rings
- A concentric layer of ring is developed annually inside trunk of a tree
- Used to determine the age of the tree (Dentro-Chronology)
- Also known as growth rings
Bark
Defined as the outside layer of trunk, branches & twigs (small offshoot branches generally leafless), & are of two types, namely, inner bark & outer bark.
- The inner layer of bark is made up of living cells known as Phloem, which carry sap full of sugar from the leaves to the rest of the tree.
- The outer bark is made up of dead cells, like our nails, which serves as a protective layer of the tree
- A number of products are made from the bark of a tree namely Latex, Cinnamon, Perfumes, Poison etc.
Cambium
- Thin layer of living cells just inside the bark
- It is the part of the tree that makes new cells allowing the tree to grow wider each year.
Sapwood (Xylem)
- Made up of a network of living cells that bring water & nutrients up from the roots to the branches, twigs & leaves.
- It is the youngest wood of the tree, over the years, inner layers of sapwood die & become heartwood.
Heartwood
- Dead sapwood in center of the trunk, usually darker than sapwood.
- It is the hardest wood of the tree giving it support & strength.
Pith
- Tiny dark spot of spongy living cells right in the center of the tree trunk
- Transports the essential nutrients throughout the tree