Naxalism – Left Wing Extremism
Spread to 17 states in India, including Assam, Bihar, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Orissa, Uttar Pradesh, West Bengal to name the few main one.
Naxalites operate in a vacuum created by inadequacy of administrative and political institutions, and seek to offer an alternative system, of governance which promises emancipation of these segments from the clutches of ‘exploiter’ classes through the barrel of a gun.
[clear]Causes
- Inequality in rural India based on unequal distribution of land
- Low literacy levels along with poverty & unemployment
- In 2006, Forest Rights Act was enacted. But Forest Bureaucracy continued its hostility towards it.
- Politically the tribals are very poorly represented in the democratic process
- Mining contributed to misery of tribals – 40% of the total population displaced postindependence due to development of mines.
Government Approach
- Modernization of police forces + Fortification of 400 police stations in affected districts
- Developments
- focusing on infrastructure creation via. Additional Central Assistance scheme & Road Requirement Plan scheme
- Universal Service Obligation Fund supported Scheme of Mobile Services to increase mobile connectivity
- Schemes like Roshni for skill development of rural poor youth
- facilities of residential schools to children
- To improve public perception of state’s commitment towards their welfare, states have been asked to effectively implement provisions of PESA, 1996 on priority, which –
- categorically assigns rights over minor forest produce to Gram Sabhas
- funds are provided to security forces under Civil action program for conducting welfare activities in their deployment areas.
- Surrender-Cum Rehabilitation policy for Naxalites in affected areas
Assessment of Government’s Strategy
- a decrease in violent incidents and number of deaths in recent years
- a considerable decline in Maoist activities due to killing of top leaders in encounters with security forces, arrests, shortage of funds, arms and ammunitions, surrender and rehabilitation programme
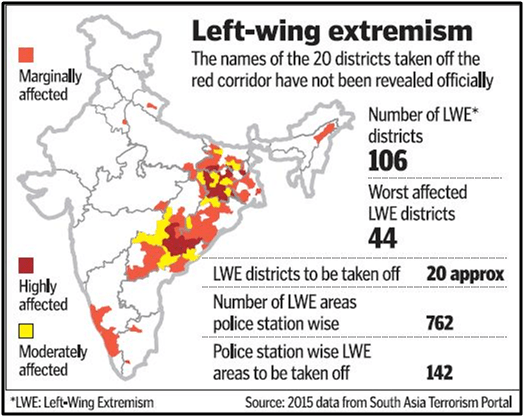
- government has also been considering the redrawing of red corridor and reducing the number of Maoist affected districts by about a fifth
Strategies to Tackle Radicalization
- Formation of “extremism counselling hotline” similar to Austria – enable parents, teachers and friends of “vulnerable and indoctrinated” youth to seek professional help for their “deradicalization”
- Big data analytics can be used to discern the level of radicalisation of potential recruits
- Religious leaders should be encouraged to counsel against radicalization
- Imparting academic knowledge as well as an understanding about what the Quran actually teaches
- Government should reach out to the minority community and win their hearts at all costs – start with the schools by imparting education of all religions & what they actually teach
Way forward
- Centre and states should continue with their coordinated efforts where Centre should play a supportive role with state police forces taking the lead.
- Undertaking technological solutions such as use of mini-UAVs or small drones to minimize loss of lives of security personnel
- Prisoners should be given considerate treatment and efficient rehabilitation.
- Inclusive developmental programmes
Operation ‘SAMADHAN’
- Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA)’s answer to the Naxal problem
- Smart leadership – states to “take ownership” of anti-Naxal operations & frame strategies to counter Naxals
- Aggressive strategy – More helicopter support for operations + 400 fortified police stations
- Motivation and training – to train forces to take on Naxals
- Actionable intelligence – Better inter-state coordination and intelligence sharing
- Dashboard Based KPIs (key performance indicators) and KRAs (key result areas)
- Harnessing technology –UAVs and drones for maoist hotbed areas + GPS tracking + satellite imagery
- Action plan for each theatre
- No access to financing – to ensure effective choking of fund flow to LWE groups