Photosynthesis
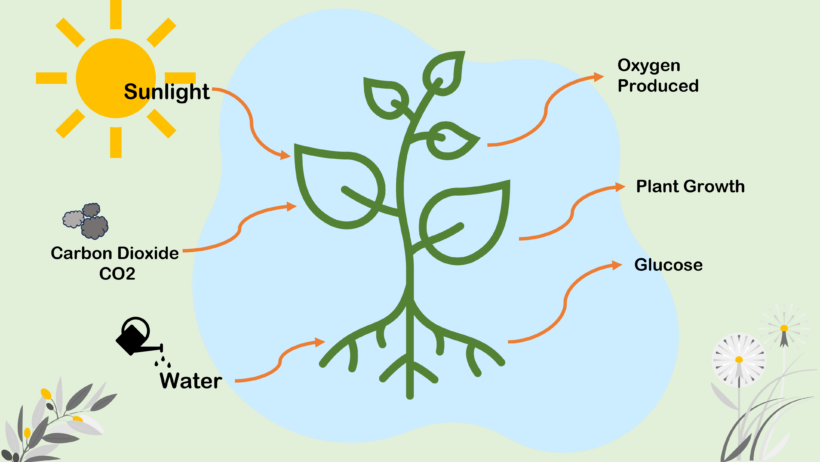
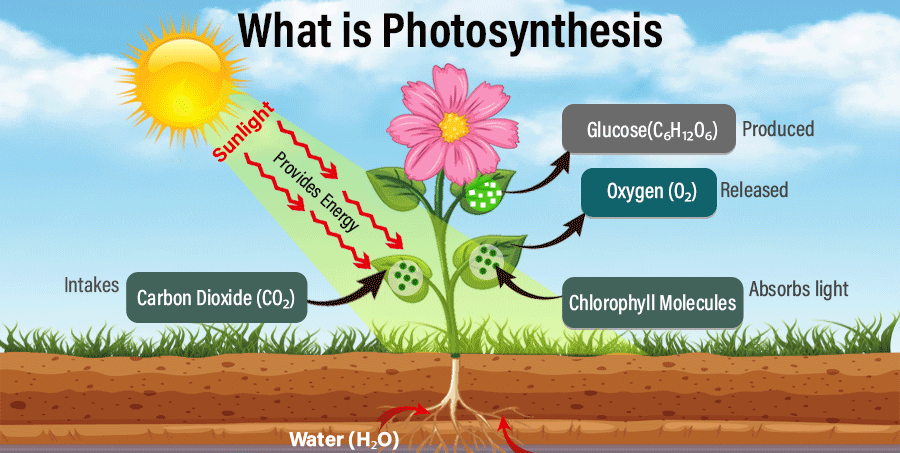
Photosynthesis is a chemical process that converts carbon dioxide into organic compounds, especially sugars, using the energy from sunlight. Photosynthesis occurs in plants, algae and many species of bacteria, but not in archaea. Photosynthetic organisms are called photoautotrophs, since they can create their own food. In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, photosynthesis uses carbon dioxide and water, releasing oxygen as a waste product.
Photosynthesis is vital for all aerobic life on Earth. In addition to maintaining normal levels of oxygen in the atmosphere, photosynthesis is the source of energy for nearly all life on earth, either directly, through primary production, or indirectly as the ultimate source of the energy in their food, the exceptions being chemoautotrophs that live in rocks or around deep sea hydrothermal vents.
The overall process is best shown by the net equation 6CO2 + 6H2O == C6H12O6 + 6O2.
🌿 Photosynthesis – 30 Important Points
✅ Basics of Photosynthesis:
-
Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants make their own food.
-
It occurs mainly in the leaves of plants.
-
The process takes place in chloroplasts, which contain chlorophyll.
-
Chlorophyll is a green pigment that captures sunlight.
-
The main raw materials for photosynthesis are carbon dioxide and water.
-
The main product is glucose (sugar), and oxygen is released as a byproduct.
-
The overall chemical equation is:
6CO₂ + 6H₂O + sunlight → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂ -
It is a type of anabolic reaction, where simple substances form complex ones.
-
It is essential for the survival of almost all life on Earth.
-
Photosynthesis occurs in two stages: the light-dependent and light-independent (Calvin cycle) reactions.
✅ Light-dependent Reaction:
-
Takes place in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts.
-
Requires sunlight directly.
-
Water molecules are split in a process called photolysis.
-
Oxygen is released during this stage.
-
Produces ATP and NADPH, which are used in the next stage.
✅ Light-independent Reaction (Calvin Cycle):
-
Takes place in the stroma of chloroplasts.
-
Does not require direct sunlight.
-
Uses ATP and NADPH from the light reaction.
-
Converts carbon dioxide into glucose.
-
This stage is also called carbon fixation.
✅ Importance of Photosynthesis:
-
Produces oxygen needed for respiration in animals and humans.
-
Maintains the balance of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
-
It is the primary source of food and energy for all living organisms.
-
Helps in regulating Earth’s climate by removing CO₂.
-
Base of all food chains and ecosystems.
✅ Other Facts:
-
Algae and some bacteria also perform photosynthesis.
-
Photosynthesis is affected by light intensity, temperature, and CO₂ concentration.
-
Stomata in leaves allow the exchange of gases during photosynthesis.
-
Without photosynthesis, life on Earth would not exist.
-
It plays a crucial role in the carbon cycle and global oxygen cycle.
-
Photosynthesis helps plants grow by converting light energy into chemical energy stored in glucose.
-
The process of photosynthesis is crucial for agriculture, as it supports crop growth and food production.
-
Cyanobacteria (blue-green algae) are among the earliest organisms known to have performed photosynthesis.
-
Artificial photosynthesis is being researched as a way to generate clean energy and reduce carbon emissions.
-
Chloroplasts contain grana (stacked thylakoids) that increase surface area for capturing light energy.
-
Photosynthesis contributes to the formation of biomass, which serves as fuel for ecosystems.
-
The rate of photosynthesis can be measured by observing the production of oxygen or the uptake of carbon dioxide.
-
Artificial photosynthesis aims to mimic natural photosynthesis processes to produce renewable energy and reduce environmental impact.
For more updates, visit www.iasmania.com. Please share your thoughts and comments.
If you’re passionate about building a successful blogging website, check out this helpful guide at Coding Tag – How to Start a Successful Blog. It offers practical steps and expert tips to kickstart your blogging journey!