Autotrophs & Heterotrophs
The biotic or the living components of the ecosystem are divided into two categories Autotroph and Heterotroph. Let us read about them in detail.
Autotrophs
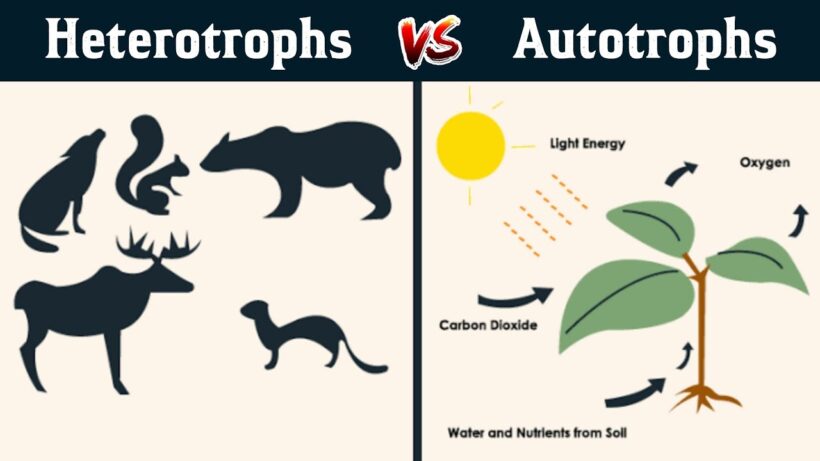
Autotrophs are those organisms that are capable of synthesizing their own food, using the energy from the sun, by a process known as photosynthesis. All plants and some forms of bacteria come under this category. They are also known as producers in a food chain, as they are able to produce their own food and this food is directly or indirectly used by other members of the food chain.
Autotrophs are self-feeding or self-sustaining members of the ecosystem. They synthesize complex organic compounds such as carbohydrates, proteins and fats, from simple inorganic molecules, with the help of light energy or by inorganic chemical reactions. Depending on the method by which they synthesize their food, autotrophs are further classified into two categories:
- Phototrophs – These are mostly plants that use light as source of energy.
- Chemoautotrophs – Bacteria or fungi that obtain their food by inorganic chemical reaction.
Heterotrophs
Those organisms which obtain energy from organic molecules that are made by autotrophs are known as heterotrophs. These organisms fail to synthesize their own food and are dependent on the producers or autotrophs, for the supply of organic compounds required for their growth. As heterotrophs obtain energy from producers, they function as consumers in the food chain.
The complex organic compounds that are produced by the autotrophs are broken down into simple substances, that provide energy to the heterotrophs. Like autotrophs, heterotrophs are also classified as photoheterotrophs and chemoheterotrophs, depending on the energy source. Consumers are further classified into different categories, based on their mode of consumption.
- Herbivores – A heterotroph that obtains energy directly from plants.
- Carnivores – Those animals which feed on other animals.
- Omnivores – Animals that obtain their food from plants as well as from other animals.
- Saprobes – Organisms that obtain energy by breaking down remains of dead plants and animals.
🌱 Autotrophs & Heterotrophs – 25 Key Points
🔹 Autotrophs:
-
Autotrophs are organisms that produce their own food.
-
They use light or chemical energy to create organic compounds.
-
The process used by autotrophs is known as autotrophic nutrition.
-
The most common type of autotrophs are plants.
-
Photosynthesis is the main method of food production in photoautotrophs.
-
Chemoautotrophs make food using chemical energy from inorganic substances.
-
Examples of autotrophs: plants, algae, and some bacteria.
-
Autotrophs are also called producers in a food chain.
-
They convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
-
Autotrophs form the base of the food chain.
-
They play a vital role in maintaining oxygen levels in the atmosphere.
-
They are essential for life on Earth by supporting heterotrophs.
🔹 Heterotrophs:
-
Heterotrophs cannot make their own food.
-
They depend on other organisms for nutrition.
-
Heterotrophic nutrition involves consuming autotrophs or other heterotrophs.
-
Examples: animals, fungi, protozoa, and most bacteria.
-
Heterotrophs are also known as consumers in the food chain.
-
They can be herbivores, carnivores, omnivores, or decomposers.
-
Heterotrophs obtain energy by breaking down complex food molecules.
-
They play a role in nutrient cycling and decomposition.
-
Humans are heterotrophs.
-
Without autotrophs, heterotrophs would not survive.
🔹 Comparison:
-
Autotrophs use inorganic sources to make food; heterotrophs need organic food sources.
-
Autotrophs release oxygen as a byproduct; heterotrophs use oxygen in respiration.
-
Both are essential to maintain the balance of ecosystems and energy flow.
For more updates about Autotrophs & Heterotrophs, visit www.iasmania.com. Please share your thoughts and comments.
If you’re passionate about building a successful blogging website, check out this helpful guide at Coding Tag – How to Start a Successful Blog. It offers practical steps and expert tips to kickstart your blogging journey!