Antigen & Antibody
While discussing about ‘self’ and ‘non-self’, we got a broad idea of antigen.
Definition and Properties of an antigen
An antigen is any foreign molecule that can trigger a specific immune response. Most antigens are either proteins or very large polysaccharides. Another term ‘immunogen’ is also used for antigen. However, there is a slight difference between the two.
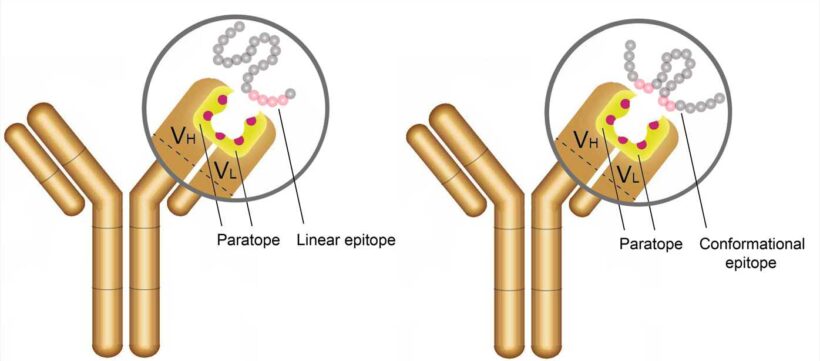
Paratopes and Epitopes: The part of antibody molecule which makes contact with the antigen is termed the paratope. The part of antigen molecule that makes, contact with paratope is called the epitope. There may be a series of epitopes on on an antigen. Such epitope clusters are called ‘antigenic determinant’.
Requirements for becoming an antigen
- Substance should be foreign to the host.
- Molecular weight of molecule should be 10,000 Dalton or more.
- It should possess chemical complexity.
Antigens are often proteins or polysaccharides, and each one has specific regions called epitopes – these are the precise parts that immune cells recognize and bind to. The body views antigens as “non-self” and creates antibodies to fight them.
There are two main types of antigens:
-
Exogenous Antigens – Enter the body from the outside (e.g., pathogens, allergens).
-
Exogenous Antigens – Generated within the body (e.g., viral proteins produced inside infected cells or cancer cell markers).
Some antigens can also be autoantigens—normal body proteins that are mistakenly targeted by the immune system, leading to autoimmune diseases (e.g., Type 1 diabetes, lupus).
Antibody: Definition and properties
Antibody is a protein molecule produced in animals in response to an antigen. Antibodies belong to the category of proteins called immunoglobulin. Each antibody molecule is composed of four interlinked polypeptide chains.
The two long chains are called heavy chains, and the two short chains are called light chairs An antibody has a “stem” called “Fc” portion which comprises the lower half of the two heavy chains and two “prongs” (the amino acid sequences that bind antigen”.
The amino acid sequences of Fc portioff are identical (constant) for all antibodies of same class. In contrast amino acid sequences for antigen binding site vary from antibody to antibody in a given class.
Antigen-Antibody Interaction
The interaction between an antigen and an antibody is highly specific, much like a key fitting into a lock. This specificity allows the immune system to recognize and remember pathogens, forming the basis for immunity.
After an initial infection or vaccination, the immune system “remembers” the antigen and can respond more rapidly and effectively if it encounters it again.
This antigen-antibody relationship is also the foundation of many diagnostic tests and vaccines. For example, COVID-19 tests often detect either viral antigens or antibodies produced in response to the virus.
🔬 Real-World Applications of Antigen-Antibody Reactions (Continued)
-
Autoimmune Disease Diagnosis
-
Tests like ANA (antinuclear antibody) and RF (rheumatoid factor) detect autoantibodies that attack the body’s own tissues. These are used to diagnose autoimmune diseases such as lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
-
-
Organ Transplant Compatibility Testing
-
HLA (Human Leukocyte Antigen) typing uses antigen-antibody reactions to match donors and recipients, reducing the risk of organ rejection. Antibody screening also helps detect pre-formed antibodies that might attack the transplanted organ.
-
-
Allergy Testing
-
Allergy tests use IgE antibodies to detect hypersensitivity to specific allergens like pollen, food, or insect stings. The presence of allergen-specific IgE helps confirm allergic conditions.
-
-
Cancer Treatment and Diagnosis
-
Monoclonal antibodies are used to target specific antigens on cancer cells (e.g., HER2 in breast cancer). Some are labeled with radioactive substances for immunotherapy or immuno-imaging.
-
-
Blood Group Typing & Cross-Matching
-
Blood banks use antigen-antibody reactions to determine a person’s blood type (ABO and Rh) and to cross-match donor and recipient blood for transfusions, ensuring compatibility and preventing immune reactions.
-
For more updates about Antigen & Antibody, visit Science Topics. Please share your thoughts and comments.